This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
How to Increase VO2 Max (& Why You Should)
October 23, 2024

VO2 max is a key metric for evaluating cardiovascular fitness, endurance and overall health. Whether you’re a professional athlete, fitness enthusiast or someone looking to improve her health, understanding and increasing your VO2 max can lead to better performance and health benefits.
In this article, we’ll explore what it is, how it’s measured and why increasing it can be a game-changer.
What is VO2 max?
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen consumption, refers to the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use during intense exercise. It’s a crucial indicator of aerobic endurance, reflecting how efficiently your heart and lungs deliver oxygen to your muscles during activity.
In simpler terms, it measures how well your body uses oxygen to fuel physical performance.
The term “VO2” stands for volume of oxygen, and “max” indicates the maximum capacity. This number is typically expressed in milliliters of oxygen consumed per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min).
How is VO2 max measured?
VO2 max is typically measured in a lab or clinical setting through a graded exercise test, where an individual runs or cycles while wearing a mask connected to a machine that measures oxygen consumption.
The test increases in intensity until exhaustion, and the machine calculates the highest volume of oxygen consumed at peak exertion.
While lab testing provides the most accurate results, various methods can estimate VO2 max, such as:
- VO2 Max Calculator: Online tools that estimate VO2 max based on factors like heart rate, age, weight and exercise intensity. These calculators are less precise but convenient.
- Wearable Devices: Many fitness trackers and smartwatches estimate it using heart rate and activity data during workouts.
- VO2 Max Chart: Charts that estimate VO2 max by age and activity level, giving you a rough idea of where you stand compared to average levels in your demographic.
Submaximal exercise tests are another common way to estimate it. These tests involve physical activities that are less intense than a person’s maximum effort, typically measuring heart rate responses at submaximal workloads.
The data gathered can then be extrapolated to predict VO2 max.
Submaximal tests are less strenuous and safer for most individuals, especially those who are untrained, elderly or have certain health conditions. They are also easier to administer compared to maximal tests that require subjects to exercise to their limits.
While submaximal tests do not directly measure VO2 max, they provide a fairly accurate estimate, especially when combined with known equations and formulas.
During a submaximal test, the subject exercises at a specific intensity (usually a fixed percentage of their maximum heart rate) for a set duration or until a target heart rate is reached.
The tests are based on the relationship between heart rate and oxygen consumption: As exercise intensity increases, both heart rate and oxygen uptake rise linearly.
Common submaximal tests include:
Astrand-Rhyming Cycle Ergometer Test:
- Performed on a stationary bike.
- The test lasts 6 minutes at a set workload, with heart rate recorded during the last minute.
- A nomogram is used to estimate VO2 max based on heart rate and workload.
- A multistage test where the workload is gradually increased every 3 minutes.
- Heart rate is monitored, and VO2 max is predicted from heart rate at two submaximal workloads.
- Involves walking 1 mile as fast as possible.
- After the walk, heart rate is recorded along with time taken to complete the mile, and VO2 max is estimated using a formula.
- Involves stepping up and down on a platform for a set period (usually 3 minutes).
- Heart rate is measured immediately after the test, and VO2 max is estimated from the recovery heart rate.
- Performed on a treadmill with progressively increasing intensity.
- Heart rate is tracked at different speeds or inclines to estimate VO2 max.
What is a good VO2 max?
A “good” VO2 max varies by age, gender and fitness level.
Typically, higher values indicate better cardiovascular fitness and endurance. For example, elite athletes often have much higher VO2 max values than the average person.
Below is a general VO2 max chart that outlines typical values by age:
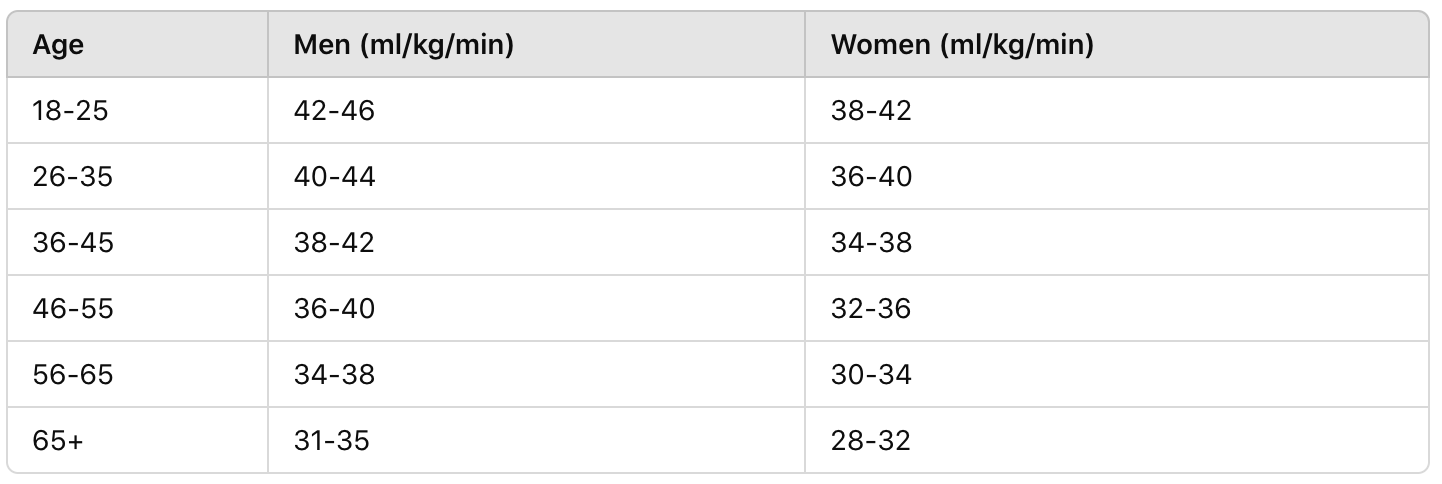
A good VO2 max score depends on your goals and fitness aspirations. For most people, improving from a lower to a moderate or high range can result in significant health and endurance benefits.
How to increase VO2 max
Improving VO2 max involves training your cardiovascular system to become more efficient at utilizing oxygen. Here are the most effective strategies to boost yours:
1. High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
HIIT involves alternating between short bursts of intense exercise and periods of lower intensity or rest. Research shows that HIIT workouts can significantly increase VO2 max in a shorter time compared to steady-state cardio.
Aim for 20–30 minutes of HIIT sessions 2–3 times a week.
2. Long, steady-state cardio
While HIIT is great for rapid improvements, longer steady-state cardio sessions at moderate intensity also improve VO2 max.
Activities like running, cycling and swimming at 60%–70% of your max heart rate for 45–60 minutes can gradually enhance your aerobic capacity.
3. Incorporate interval running
Interval running combines both speed and endurance training. Running 400-meter or 800-meter repeats at your maximum sustainable pace with recovery in between can help you increase VO2 max by challenging both your aerobic and anaerobic systems.
4. Strength training
While cardiovascular training is the primary driver of VO2 max improvements, adding strength training can help by improving overall muscular efficiency. This, in turn, reduces oxygen demand for a given workload, making your body more efficient.
5. Increase training volume gradually
Progressively increasing the volume and intensity of your workouts over time is key. Aim to slightly increase your running or cycling distance, or add more repetitions to your intervals each week to challenge your aerobic system continuously.
6. Improve breathing techniques
Optimizing your breathing patterns during exercise, such as practicing diaphragmatic breathing, can help you increase oxygen intake, which can enhance VO2 max.
Breath-focused exercises like yoga or pilates can also help improve lung capacity.
Why you should improve your VO2 max
1. Better endurance
A higher VO2 max allows you to sustain higher intensities for longer, whether you’re running a marathon, cycling or playing sports.
2. Improved cardiovascular health
VO2 max is closely linked to heart and lung health. Increasing yours improves your heart’s efficiency, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
3. Weight management
Higher-intensity workouts that improve VO2 max burn more calories, helping with weight loss or maintenance.
4. Enhanced athletic performance
For athletes, increasing VO2 max can lead to better race times and overall performance.
5. Increased life span
Research has shown that higher levels are associated with greater longevity and lower risks of age-related diseases.
Conclusion
- VO2 max is one of the best measures of aerobic fitness and overall health.
- While genetics play a role in determining your VO2 max, you can still make significant improvements through targeted training. High-intensity interval training, steady-state cardio, strength training and proper breathing techniques are all effective ways to increase yours.
- By doing so, you’ll boost your endurance, cardiovascular health and athletic performance.
- Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, increasing your VO2 max should be a priority for long-term health and performance.
- Start incorporating HIIT and steady-state cardio into your routine today, and track your progress with a VO2 max calculator or a fitness tracker.
- By focusing on these strategies, you’ll be well on your way to optimizing your aerobic capacity and unlocking your body’s full potential.



