This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Citron Fruit Benefits Immunity, Heart Health & More
April 2, 2018

There’s no doubt that citrus fruits are good for you. Fruits like oranges, lemons, limes and grapefruit top the charts when it comes to their antioxidant content, nutritional profile and natural health-promoting properties. But have you ever heard of citron fruit?
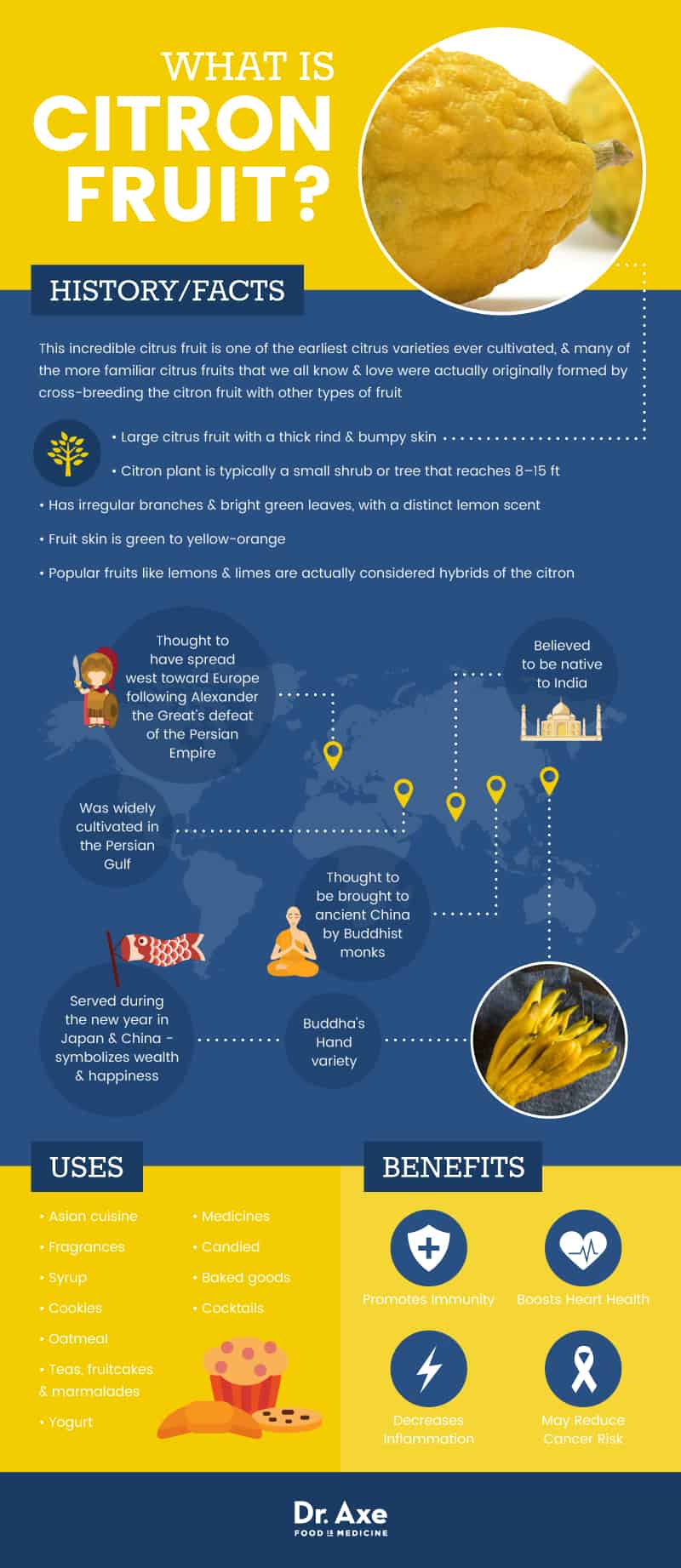
This incredible citrus fruit is one of the earliest citrus varieties ever cultivated, and many of the more familiar citrus fruits that we all know and love were actually originally formed by cross-breeding the citron fruit with other types of fruit. Still, few people have ever heard of, let alone tried, this nutrient-rich fruit.
Rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, plus incredibly delicious and flavorful, there are plenty of reasons to give the citron fruit a shot to take advantage of the unique health benefits that it has to offer.
What Is Citron Fruit?
Citron fruit, also known as Citrus medica, is a large citrus fruit with a thick rind and bumpy skin. The citron plant is typically a small shrub or tree that reaches between eight and 15 feet tall. The citron tree has irregular branches and bright green leaves with a distinct lemon scent. The fruit itself has skin ranging in color from green to yellow-orange. It has a very thick, leathery rind with minimal amounts of flesh, which sets it apart from other citrus fruits.
There are also other variations of the citron fruit available, such as “Buddha’s hand,” a type of citron fruit with long, finger-like projections that is commonly grown throughout China.
Interestingly, citron fruit is considered one of the original types of citrus fruit through which other types of fruit later developed through hybridization. Even popular fruits like lemons and limes are actually considered hybrids of the citron fruit.
In addition to being widely used in many types of Asian cuisine, citron fruit is also a common ingredient in many fragrances and medicines. Because of the unique flavor of the rind, it is often candied and added to foods like teas, fruitcakes and marmalades.
Nutrition Facts
Like other citrus fruits, citron is high in vitamin C and antioxidants. In particular, citrus fruits and their peels are generally high in antioxidant compounds and bioflavonoids, such as (1, 2):
- Hesperidin
- Naringin
- Hesperetin
- Naringenin
- Limonene
- Linalyl acetate
- Linalool
Citron is also an excellent source of pectin, a type of soluble fiber that absorbs water and can be easily metabolized by the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Thanks to the powerful nutrients found in the citron fruit, this unique citrus fruit has been associated with a number of potential health benefits, from a reduced risk of chronic disease to enhanced immunity and beyond.
Benefits
1. Promotes Immunity
The immune system plays a pretty big role in your overall health; it fights off foreign invaders and works hard to keep harmful bacteria, viruses and fungi out of the body to prevent disease. Whether you’re feeling a bit under the weather or starting to come down with a case of the sniffles, a serving or two of citron fruit may be able to help by providing a concentrated dose of both vitamin C and antioxidants.
A review published in the Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism showed that getting enough vitamin C can reduce symptoms and shorten the duration of respiratory tract infections like the common cold. It may also be useful in preventing and improving outcomes for conditions like pneumonia, malaria and diarrhea. (3) Antioxidants, meanwhile, can help protect against oxidative stress and prevent damage to your immune cells. (4)
Be sure to combine citron fruit with some other natural immune boosters, such as elderberry extract, probiotics and ginger, to keep your immune system running smoothly.
2. Decreases Inflammation
Although acute inflammation is a normal response by the immune system designed to help protect the body against infection, chronic inflammation can take a serious toll on your health and is believed to contribute to chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. (5) One of the main causes of inflammation is a buildup of harmful free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can cause damage to your cells.
Like other citrus fruits, citron fruit is loaded with antioxidants that can help neutralize free radicals and decrease inflammation. A test-tube study out of Korea actually found that treating cells with citron essential oil was able to decrease several markers of inflammation. (6) Citron fruit is also rich in vitamin C, an important micronutrient with antioxidant properties that has also been shown to help relieve inflammation. (7)
Besides citron fruit, other anti-inflammatory foods that you should eat include leafy green vegetables, beets, broccoli and blueberries.
3. May Reduce Cancer Risk
What you put on your plate can have a major impact on many aspects of health, including the risk of cancer development. Citron fruit is packed with important micronutrients, carotenoids and antioxidants that may be beneficial when it comes to cancer prevention.
Multiple studies have found that a higher intake of citrus fruits could be associated with a lower risk of cancer. One analysis comprising nearly 13,000 people found that eating more citrus fruits was linked to a lower risk of cancers of the digestive and upper respiratory tract. (8) Another study also found that a high intake of citrus fruits was associated with a 10 percent lower risk of breast cancer. (9)
For best results, pair citron fruit with a diet rich in other cancer-fighting foods, such as cruciferous vegetables, mushrooms, berries and cultured dairy products.
4. Boosts Heart Health
Heart disease is a problem that affects millions around the globe. In fact, according to a recent 2017 report, heart disease is responsible for 31.5 percent of all deaths worldwide, and it’s estimated that 44 percent of the United States population will have some form of heart disease by the year 2030. (10)
Studies show that loading up on citrus fruits like citron may help keep your heart in tip-top shape and protect against heart disease. A study published in the Journal of Epidemiology showed that frequent consumption of citrus fruits was associated with a lower risk of heart disease and stroke among 10,623 people. (11) Another recent 2017 study had similar findings, reporting that a higher intake of citrus fruits was linked to a lower risk of heart disease and even death. (12)
In addition to citrus fruits like citron, fill up your plate with other heart-healthy foods like salmon, oats, avocado and whole grains.
Citron Fruit vs. Yuzu Fruit vs. Lemon vs. Lime
Citron fruit, yuzu fruit, lemons and limes are all types of citrus fruits that belong to the same genus of plants. They share similarities in their impressive nutrient profiles, distinctive tastes and vibrant color palettes. They are also often used similarly in recipes and can be all used to add a zing of flavor to desserts and beverages alike.
However, there are some unique differences that set these citrus fruits apart. The most obvious is in their appearance. Citron is slightly larger than the other fruits and has bright yellow skin when it’s at peak ripeness. While there are some notable similarities between the appearance of the citron vs. lemon, the citron fruit is generally larger with a bumpier texture and thicker rind.
Lemons and limes are widely used around the world and easy to incorporate into a variety of dishes. Meanwhile, the rind, fruit and zest of the yuzu fruit is common in many parts of Japan and Korea.
Citron fruit, on the other hand, has a thick, leathery rind that is difficult to separate from the segments of fruit as well as a relatively dry, flavorless pulp that’s different than most other citrus fruits. For this reason, the citron fruit is typically used for its rind, which is often candied or used to make honey citron tea.
Where to Find Citron and How to Pick the Best One
Finding citron fruit for sale can be a challenge, but it’s far from an impossible feat. Check in the produce section of your local specialty store, or try a farmers market instead. If you still don’t have any luck, some produce suppliers will ship fresh citron fruit directly to you for a fee. Candied citron and citron marmalade are much easier to find and are available at most grocery stores as well as online retailers.
When buying fresh citron, make sure it has a strong smell, and look for rinds that are blemish-free with no soft or tender spots on the skin. The color should be bright yellow; green skin indicates that it hasn’t reached ripeness while a darker yellow-orange means that the fruit is overripe. Once you get it home, you can store it on the counter at room temperature for up to a week or in the refrigerator for two to three weeks.
Uses and Recipes
Unlike other types of citrus fruit, citron fruit has a thick rind and very little flesh and seeds. Most recipes involve cutting the rind into small pieces, cooking it in sugar syrup, or caramelizing it and then making it into a marmalade or adding it to baked goods. Candied citron can be mixed into cookies and fruit cakes, added to cocktails, sprinkled over oatmeal or used to sweeten up a bowl of probiotic yogurt.
You can also use citron in your favorite honey citron tea recipe. Honey citron tea is made by combining slices of citron fruit with sugar and honey to make a preserve, which is then mixed with hot water. It can be consumed both hot and cold and is often used to soothe sore throats. If you’re looking for where to buy honey citron tea, you can find the preserves (sometimes called “yuja-cheong”) made from either citron or yuzu fruit in most Asian specialty markets. You can also try making it at home if you have some fresh citron fruit on hand.
History
Citron fruit has been grown and cultivated since ancient times, even longer than most other species of citrus fruits. Believed to be native to India, it’s said that the citron fruit was originally brought to ancient China by Buddhist monks. It was also widely cultivated in the Persian Gulf and is thought to have spread west toward Europe following Alexander the Great’s defeat of the Persian Empire.
In the Bible, Leviticus mentions that citron fruit (or “fruit of the tree hadar”) is part of the Feast of Tabernacles, a traditional Jewish holiday typically celebrated annually sometime between late September and late October.
The fruit was also described by Roman author Pliny the Elder, who stated: (13)
As to the fruit, it is never eaten, but it is remarkable for its extremely powerful smell, which is the case, also, with the leaves; indeed, the odour is so strong, that it will penetrate clothes, when they are once impregnated with it, and hence it is very useful in repelling the attacks of noxious insects.
Today, citron fruit is common in many types of Asian cuisine and is often candied and added to fruitcakes, beverages and desserts. It even still holds cultural significance for many; in fact, one of the common variations of citron, Buddha’s hand, is commonly served during the new year in Japan and China because it symbolizes wealth and happiness.
Precautions
Although relatively uncommon, it is possible to have an allergy to citrus fruits like the citron fruit. Symptoms can include itching, swelling, hives, redness and tingling.
Some people may also be allergic to citrus fruit peels, which can result in symptoms of contact dermatitis like burning, itching or dry, flaky skin. If you notice these or any other food allergy symptoms caused by citron, discontinue use immediately and consult with your doctor.
Additionally, note that candied citron is high in sugar, which may deplete the fruit of some of its health-promoting properties. Keep intake in moderation, and be sure to pair it with other fresh citrus fruits to maximize the health benefits of your diet.
Final Thoughts
- The citron fruit is a large, oblong citrus fruit with bumpy skin and a thick rind.
- Like other fruits, it’s high in vitamin C as well as an assortment of antioxidants and soluble fiber.
- Citron fruit benefits include improved immunity, decreased inflammation and enhanced heart health. Eating more citrus fruits, such as citron, has also been associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancer.
- You can often find citron fruit for sale in specialty stores or farmers markets as well as online. Candied citron and citron preserves are easier to find and typically available at most major grocery stores.
- Use citron in your favorite baked goods, brew up a cup of citron tea, or sprinkle it over oatmeal or yogurt to add a dose of flavor and health benefits.




