This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Pinto Beans Nutrition Benefits the Heart and May Help Fight Cancer
April 29, 2025

It’s easy to make jokes about different types of beans and the effects they have on flatulence, but the focus should be on just how beneficial pinto beans nutrition, for example, can be for our health.
For instance, did you know that many types of beans, such as anasazi beans and pinto beans, are some of the top cancer-fighting foods around? It’s true, but that’s not all beans do.
Pinto beans nutrition also benefits the heart and so much more.
Pinto beans nutrition facts
A half-cup serving of cooked pinto beans nutrition (about 85.5 grams) contains approximately:
- Calories: 122.5
- Total Carbohydrates: 22.4 g
- Fiber: 7.7 g
- Sugar: 0.3 g
- Total Fat: 0.6 g
- Saturated Fat: 0.1 g
- Polyunsaturated Fat: 0.2 g
- Monounsaturated Fat: 0.1 g
- Protein: 7.7 g
- Sodium: 0.9 mg (<1% DV*)
- Folate: 147 mcg (37% DV)
- Copper: 0.2 mg (22% DV)
- Manganese: 0.4 mg (17% DV)
- Thiamine: 0.2 mg (17% DV)
- Vitamin B6: 0.2 mg (12% DV)
- Magnesium: 42.8 mg (10% DV)
- Phosphorus: 125.5 mg (10% DV)
- Selenium: 5.3 mcg (10% DV)
- Iron: 1.8 mg (10% DV)
- Riboflavin: 0.1 mg (8% DV)
- Potassium: 373 mg (8% DV)
- Zinc: 0.8 mg (7% DV)
- Vitamin E: 0.8 mg (5% DV)
Pinto beans nutrition also provides some calcium, vitamin C, vitamin K, niacin, pantothenic acid and more.
*Daily Value: Percentages are based on a diet of 2,000 calories a day.
Health benefits
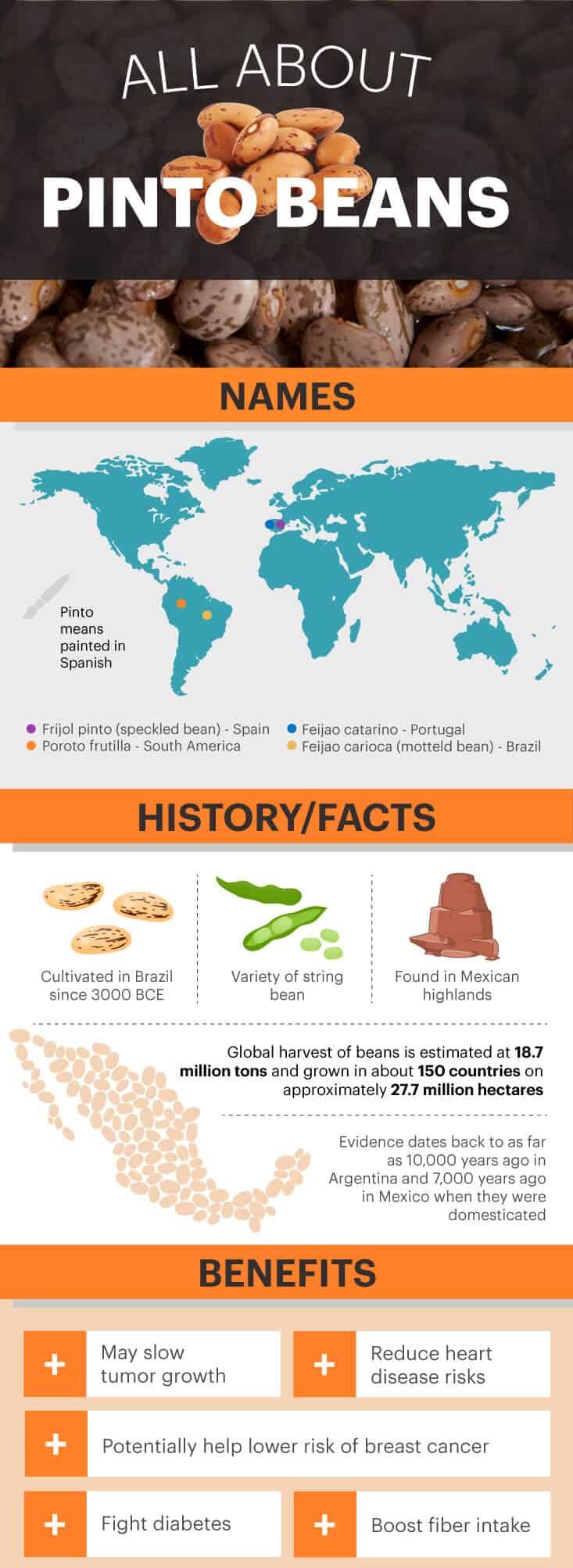
1. May help slow tumor growth
Pinto beans contain antioxidants called polyphenols, which may help prevent some forms of cancer, according to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. More specifically, pinto beans nutrition provides kaempferol, which is a flavonoid known to help reduce inflammation.
The beneficial antioxidants in pinto beans nutrition may slow the growth of tumors while increasing the survival rate of much-needed healthy cells.
Studies have found benefits of eating foods that contain kaempferol include reducing the risk of developing cancer. This is the result of the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making the pinto bean a great food for possibly preventing and even treating some diseases, even potentially cancer.
2. Can reduce heart disease risks
Pinto beans may be helpful in reducing cholesterol levels and therefore the risk for heart disease. By having about a half cup of pinto beans on a daily basis, research published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition showed that it can help reduce your total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels.
This works by replacing a protein source that’s high in fat with pinto beans, which have almost no fat. The increase in dietary fiber consumption can also help lower your cholesterol, ultimately reducing the risk for developing heart disease as a powerful cholesterol-lowering food.
3. Potentially help lower risk of breast cancer
The American Academy of Pediatrics studied premenopausal women who were asked to complete a dietary questionnaire dating back to adolescent years. The study revealed that women who had more total dietary fiber intake at an earlier age through adulthood were associated with having significantly lower breast cancer risks, suggesting that a high-fiber diet during adolescence and early adulthood may be particularly important.
Digging a little deeper, sex steroid hormone levels are known to be strongly related to breast cancer development. A diet high in fiber is thought to reduce the risk of breast cancer by inhibiting reabsorption of estrogen.
The San Francisco Bay Area Breast Cancer Study is a notable human study examining the relationship between bean consumption and tumor risk. This population-based, case-control study included 2,135 breast cancer cases and 2,571 controls from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds.
The researchers found that high intake of bean fiber and total beans was associated with a reduced risk of hormone receptor–negative breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited known risk factors. Specifically, women in the highest quartile of bean fiber intake had a 28 percent to 36 percent lower risk of developing this form of breast cancer compared to those in the lowest quartile.
While this study did not focus exclusively on pinto beans, it included them among the types of beans consumed by participants, particularly among Hispanic and non-Hispanic White women. The findings suggest that higher consumption of beans, including pinto beans, may be linked to a reduced risk of certain aggressive breast cancer subtypes in humans.
It’s important to note that while this study provides valuable insights, further research is needed to establish a direct causal relationship between pinto bean consumption and tumor growth inhibition.
4. Fight diabetes
Pinto beans may offer some help for those worried about diabetes by not only in reducing the risk, but in helping keep blood sugar levels in check.
The complex carbohydrates that pinto beans nutrition contains are useful due to a slower digestion process. This can increase fullness and satiety and help regulate glucose and insulin levels.
Additionally, the fiber they contain can help reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome, which affects glucose levels, making pinto beans the perfect addition to any diabetic diet plan.
In one study, subjects with type 2 diabetes were placed in a high-legume diet of about one cup per day. After three months, there was a notable decrease in hemoglobin A1c, indicating a reduced risk of heart disease and diabetes.
5. Provide beneficial fiber
While pinto beans nutrition is known to provide protein in our diets, these legumes are great at providing fiber too, something most U.S. diets lack. Fiber aids in relieving constipation and may reduce the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
This fiber also can help with weight loss and management, and beans like pinto beans make for a great addition to a longevity diet due to all pinto beans nutrition has to offer.
Recipes
Crockpot Turmeric and Curry Pinto Beans with Bone Broth and Kale
Serves: 6
INGREDIENTS:
- 1 pound dry pinto beans
- 6 cups bone broth (use water or vegetable broth for vegans and vegetarians)
- 1.5 teaspoons sea salt (add more if desired)
- 1 tablespoon freshly grated ginger root
- 1 teaspoon turmeric
- 1 teaspoon curry
- 3 garlic cloves, peeled and minced
- ¼ cup fresh cilantro
- ½ teaspoon cinnamon
- Fresh ground black pepper to taste
- 1 bay leaf
- 1 teaspoon apple cider vinegar
- 2 cups chopped kale or spinach
DIRECTIONS:
- Rinse and sort beans, pulling out any that don’t look good, and then place in a bowl.
- Add warm water, covering the beans by about 2 inches, and let soak overnight.
- The next morning, drain and add beans to a crockpot.
- Add 6 cups bone broth and the bay leaf.
- Add the turmeric, curry, garlic, cilantro (save a few sprigs for garnish), cinnamon, a little black pepper and vinegar.
- Cook on low for 8-9 hours or on high for about 5 hours.
- Once the beans are tender, add salt and pepper to taste.
- Place a small handful of spinach or kale in the bottom of your serving bowl or cup.
- Add one cup of beans.
- Top with a dollop of your favorite plain kefir (optional) and serve with sprig of cilantro for garnish.
Here are a couple more pinto bean recipes to try:
History
Pinto beans are similar to the cranberry bean in appearance in their dried form, as they’re beige in color with brown splotches and stripes that gave them their name “pinto,” which means painted in Spanish. However, once they’re cooked, those creative-looking, paint-like splotches disappear, leaving the beans a solid brown color.
The Spanish call them frijol pinto, meaning speckled bean, but in South America, they’re called poroto frutilla as a reference to what’s known as the strawberry bean. Furthermore, Portugal calls them feijão catarino, and Brazil calls them feijão carioca, meaning mottled bean. In fact, Brazil has been cultivating this little nutrition-packed bean since 3000 BCE, making it a staple of most meals with rice, pasta, potatoes and yams.
The pinto bean is a variety of the common bean also known as the string bean. Typical ways of consuming the pinto bean are whole or refried, and they’re the mainstay for a good burrito.
Pinto beans are often used in a spicy stew called chili con carne, though kidney beans, black beans and many others are used in this delicious stew as well.
Pinto beans have been around for centuries, and even today, some organizations and churches in the Deep South have pinto bean suppers for social gatherings. Though beans sometimes get a bad rap for their well-known, and sometimes embarrassing, gas-causing side effects, the nutritional value is vast, and they’re easy on the pocket.
What’s known as the wild common bean, scientifically labeled as Phaseolus vulgaris, still grows today in the Andes and Guatemala. However, pinto beans, as well as the great northern bean and small red and pink beans, are mainly found in Durango in the central Mexican highlands.
It’s unclear as to the exact date of the domestication of beans, though evidence dates back to archaeological as far as 10,000 years ago in Argentina and 7,000 years ago in Mexico.
Most U.S. dry beans are produced for human consumption as an important staple crop. However, they’re also used as animal feed in other parts of the world.
Risks and side effects
Pinto beans are famous for causing intestinal discomfort and flatulence, which can happen due to the large amounts of fiber and a sugar they contain. This sugar is difficult to break down during the digestion process and usually does not break down until it gets to the large intestine, where useful bacteria live. It’s this process that produces the often annoying and uncomfortable gas.
To help minimize the gas-causing properties of beans, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests soaking dried beans in water and changing the water a few times. Canned pinto beans are known to produce less intestinal gas, but make sure you rinse them to help reduce the high amounts of salt they usually contain.
Final thoughts
- Pinto beans are easy to make and can go in just about anything, from salads to burritos, wraps and soups.
- The nutritional and health benefits are phenomenal, including possible reduction in tumor growth, lowering blood sugar levels that can greatly help diabetics, reducing breast cancer risks and heart disease risks, all while offering beneficial fiber.
- If you’re looking for a nutrient-packed superfood without the added fat, try some pinto bean recipes today.




