This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Natural Corneal Abrasion Relief: How to Relieve a Scratched Eye
December 7, 2017

If you spend a lot of time outdoors, work with wood or metal or wear contact lenses, you have an elevated risk for experiencing a corneal abrasion. Pollen, dust, sand, wood and metal shavings that get into the eye can scratch the cornea, leading to intense pain, and, if left untreated, an infection and possible corneal ulcer. (1)
Fortunately, virtually all corneal abrasions are preventable! When working with wood or metal, wear appropriate safety glasses. And when hiking, lying on the beach, snowboarding or riding your bicycle, wear sunglasses or goggles to help prevent debris from getting in your eyes.
Our natural response to a foreign object in our eye is to rub it to relieve the irritation and itching. This is the worst thing you can do. The rubbing can cause the foreign object to further damage the cornea by scraping it across the eye. As tempting as it may be, the right way to remove debris from your eye is to gently flush it out with saline or water.
If you experience intense pain or blurred vision, it is essential that you seek medical attention immediately, particularly if you believe the particle may be wood, glass or metal. An eye doctor will carefully examine your eye and may prescribe pain medication or antibiotic eye drops to guard against infection.
Along with pink eye, corneal abrasions are extremely common in young children. Toys, dirt, and fingernails are the leading causes of a scratched cornea in children. To help guard against an eye injury, keep fingernails as short as possible. The challenge, of course, is like adults, the urge to rub the eyes when they hurt or itch can be intense. And keeping a child from rubbing their eyes can be exceedingly difficult. (2)
In the past, eye patches were routinely used to help speed healing — and to guard against rubbing. However, multiple studies show that eye patches may actually delay healing; increase the chance of infection; and cause more pain in the first 24 hours after the injury. Follow your physician’s advice before patching the eye. And under no circumstances should a patch be worn for more than 24 hours continuously. (3, 4)
While the majority of corneal abrasions heal without a problem — often within just a few days — some people may experience scarring that can permanently affect vision. This is why it is imperative that children and adults alike seek medical attention as quickly as possible to help ensure a positive outcome.
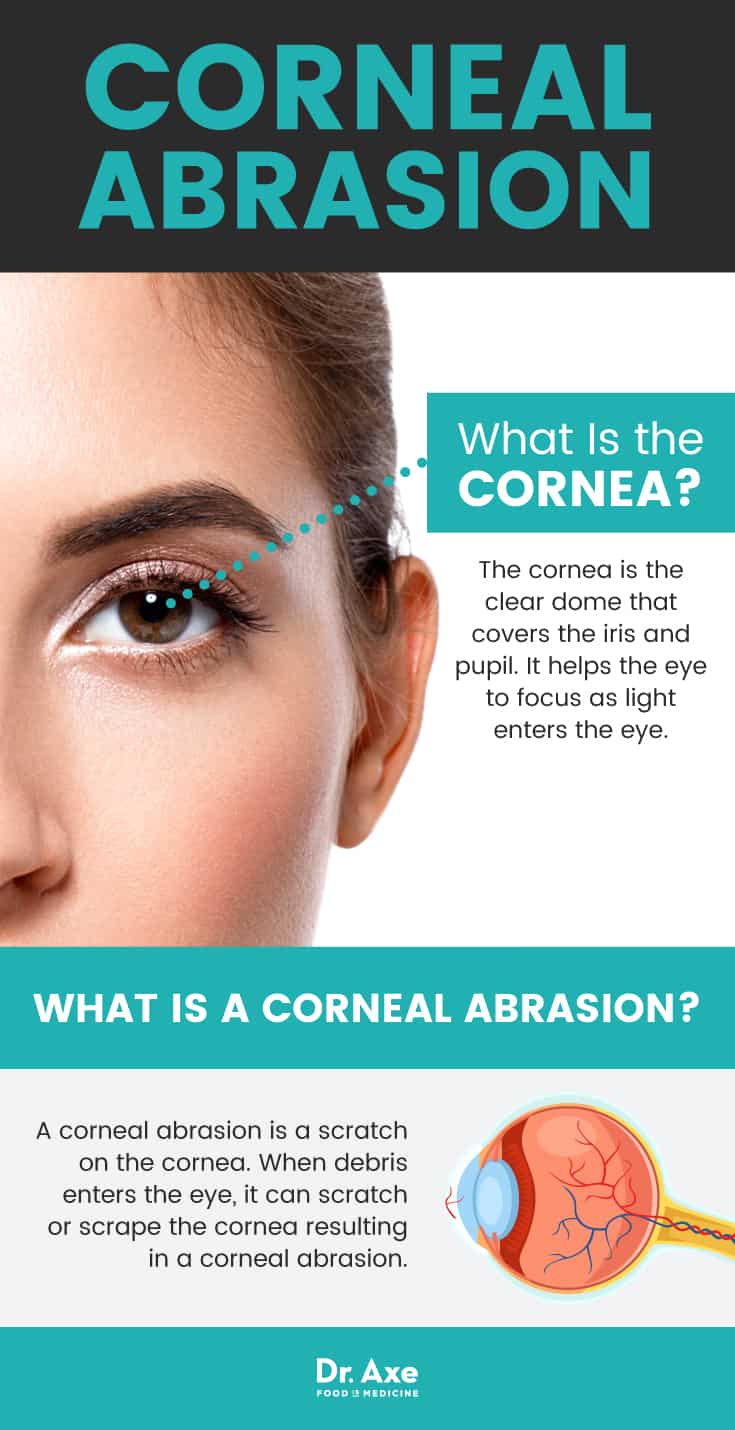
What Is a Corneal Abrasion?
The cornea is the clear dome that covers the iris and pupil. It helps the eye to focus as light enters the eye. A healthy, scratch-free and scar-free cornea is important to vision. When debris enters the eye, it can scratch or scrape the cornea resulting in a corneal abrasion. (5)
Corneal Abrasion Symptoms
- Pain, when opening or closing eye
- Feeling there is something in the eye
- Excessive tearing or watery eyes
- Redness in the eye
- Swollen eyelids
- Sudden sensitivity to light
- Sudden blurred vision
- Sudden loss of vision
- Eye twitching
- Nausea
- Headache that is dull or pulsating
Corneal Abrasion Causes & Risk Factors
The majority of scratched cornea injuries are caused by foreign matter entering the eye. Recognized risk factors include: (6)
- Working in an environment with sawdust, ash, metal shavings, dirt or glass
- Exposure to chemicals
- Participating in hockey, lacrosse, racquetball, cycling, hiking and horseback riding
- Being a miner, metal worker, woodworker or landscaper
- Rubbing eyes vigorously
- Having seasonal allergies
- Undergoing surgery under general anesthesia
- Being on a ventilator or being heavily sedated
- Being a young child with long fingernails
- Wearing soft, extended-wear lenses as they are associated with a 10 to 15-fold increase in ulcerative keratitis, a serious infection of the cornea (7)
Dangers of Corneal Abrasions
Most corneal abrasions heal without a problem in just a couple of days. However, there are complications that can arise. (8, 9, 10)
- Corneal erosions can occur at the site of the original abrasion if the cells affected don’t grow back tightly attached to the cornea. This can cause even more significant pain, and it will take additional medical intervention to ensure the eye heals properly.
- Symptoms may persist for months. If they worsen or vision is affected, see your ophthalmologist immediately.
- Dry eyes are common after an injury. Use natural eye drops to relieve dryness.
- Infection is possible
- Increasing inflammation
- Scarring of the cornea
- Corneal ulcers
- Long-term vision impairment
- Blindness
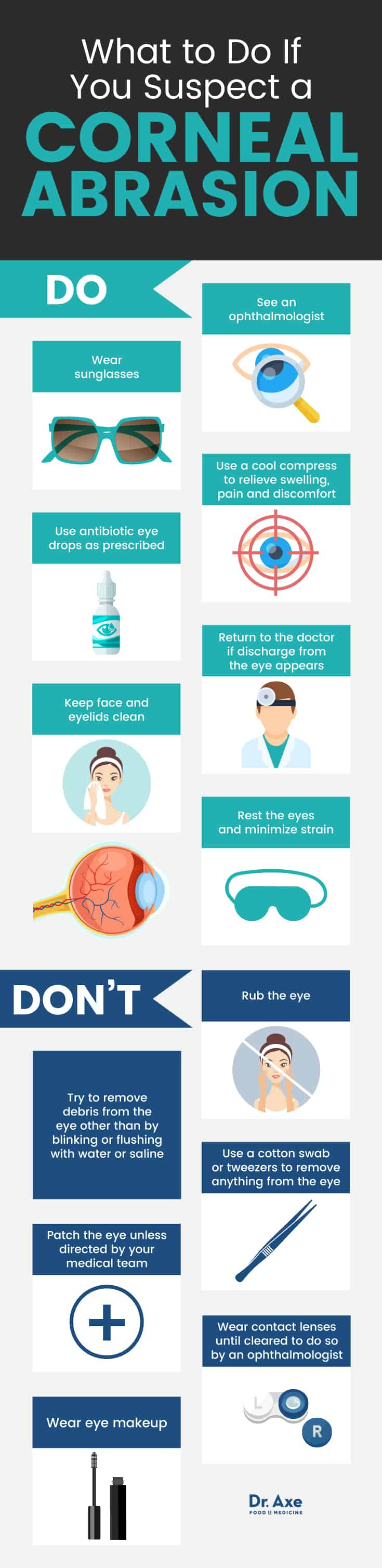
What to Do if You Suspect Corneal Abrasion
DO:
- See an ophthalmologist
- Wear sunglasses
- Use antibiotic eye drops as prescribed
- Use a cool compress to relieve swelling, pain and discomfort
- Keep face and eyelids clean
- Return to the doctor discharge from the eye appears
- Rest the eyes and minimize strain
DON’T:
- Rub the eye
- Try to remove debris from the eye other than by blinking or flushing it with water or saline
- Use a cotton swam or tweezers to remove anything from the eye
- Patch the eye unless directed by your medical team
- Wear contact lenses until cleared to do so by an ophthalmologist
- Wear eye makeup
Conventional Treatment
During an eye examination, an ophthalmologist will numb the eye with drops and use a fluorescent dye and blue light to detect damage to the cornea. If there is any debris remaining, it will be visible, and the doctor will be able to remove it safely. (11)
Most doctors will want to reevaluate their patients in 24 to 48 hours depending on the severity of the injury. This is to ensure that the cornea is healing properly and that an infection is not setting in.
After diagnosis, the doctor may recommend one or more of the following conventional treatments:
- Antibiotic eye drops or ointment to protect against infection
- Steroid eye drops to relieve inflammation
- Topical pain relievers; however, this may delay healing and is generally not recommended for contact lens wearers
- Tetanus shot, if debris was metal
6 Natural Corneal Abrasion Treatments
1. Wear sunglasses. After an injury of this type, it is not uncommon for the eyes to be sensitive to light. If you must go out into the sunlight, wear sunglasses to prevent further irritation. Indoors, fluorescent lights and overhead lights may be irritating; turn them off and opt for desk lamps with a softer tone.
2. Chamomile tea or green tea compress. Soak a chamomile tea bag or green tea bag in hot water for a minute or two, squeeze, and then place on the eye. Lean back and relax for 10 to 15 minutes. These teas have powerful antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties that may help relieve discomfort and support healing. (12)
3. Coconut oil. Known for its health benefits when consumed, coconut oil is also safe to put into the eyes. In fact, studies show that it is very similar to natural tears and provides an extra layer of protection for the eye, not to mention the benefit of its anti-inflammatory properties. With clean hands (very clean hands!) put a tiny dab of coconut oil on your pinky and place near the tear ducts. Blink, blink, blink and allow the coconut oil to move across the eye. (13)
4. Shut off technology. In the first few days after experiencing an eye injury, it is important to give your eyes plenty of time to heal. Shut off technology; staring at screens is shown to cause stress on the eyes.
5. Colloidal silver. Known for fighting a wide range of bacteria, 1 to 2 drops of colloidal silver has been shown to pick up infected cells and eliminate them from the eye. Purchase only from reputable sources and use within recommended dates.
6. Cedarwood oil: For pain, inhale cedarwood essential oil either directly from the bottle or through a diffuser. A study using mice published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found this essential oil may have analgesic and anti-inflammatory sedative properties, potentially helping to alleviate pain. (15)
Corneal Abrasion Key Points
- A corneal abrasion is one of the most common eye injuries.
- It is a very painful, sometimes excruciating, injury and left untreated infection and corneal ulcers are possible.
- The vast majority can be prevented by wearing protective eyewear.
- Sawdust, metal shards, shattered glass, dust, pollen and sand can all scratch the cornea.
- Young children are prone to eye injuries too generally caused by fingernails, dirt or toys.
- Patching of the eye, once common, is now not recommended as it can delay healing, worsen pain and increase the risk for infection.
- Do not rub the eyes, flush them instead with water or saline
- Most scratched corneas heal within 24 to 48 hours
Top Natural Treatments
- A dab of coconut oil may relieve irritation, reduce dryness and fight against infection while providing an extra level of protection for the eye.
- Green tea or chamomile tea compress may protect against infection while providing moisture and symptom relief.
- Wear sunglasses if eyes are sensitive to light.
- Allow eyes to heal for 24 to 48 hours before using technology or straining the eyes.
- Colloidal silver fights bacteria and is a recognized treatment for pink eye and other infections.
- Diffuse essential oils to relieve pain and support relaxation.


