This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Lewy Body Dementia: The Cognitive Disorder You May Not Know About
April 18, 2016

It’s a sad and widely publicized fact that comedian and actor Robin Williams’ death cause was suicide, but did you know that a commonly misdiagnosed brain disease called Lewy body dementia (LBD) is said to be the real underlying cause of his premature death?
Since Williams’ 2014 death, his wife has revealed that his last year of life was plagued by unexplained mental symptoms like delusions and anxiety as well as physical symptoms of muscle rigidity and impaired movement. Unfortunately, doctors didn’t realize that Williams was suffering from Lewy body dementia or dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) until his body was autopsied.
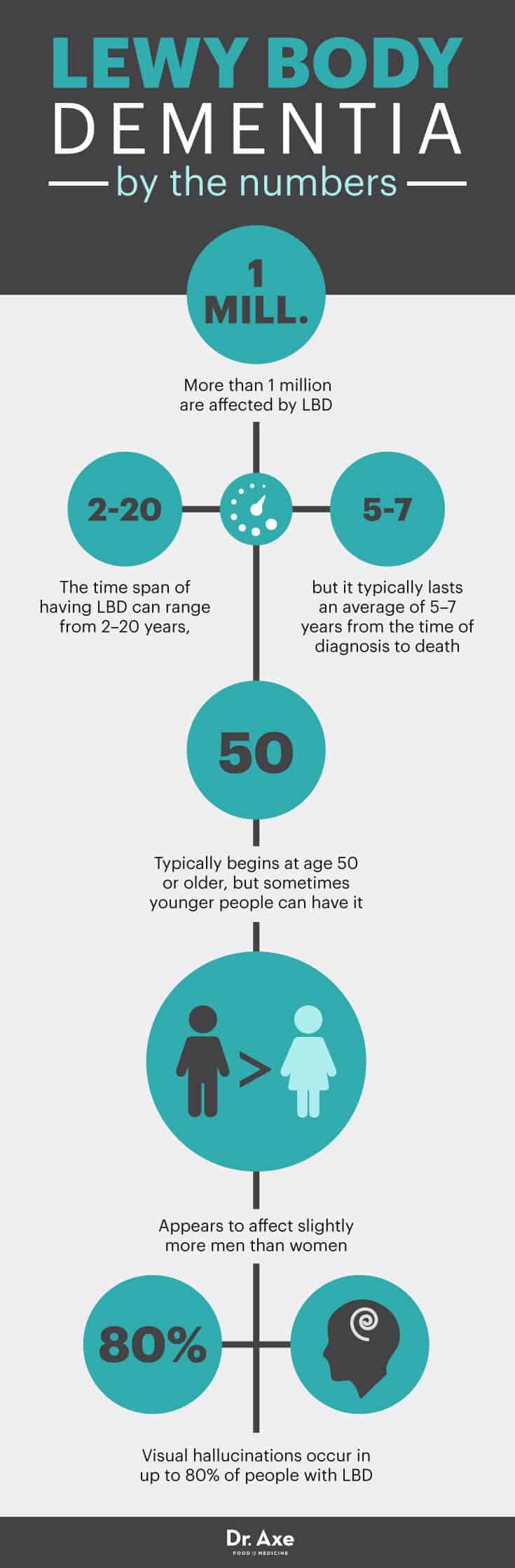
Lewy body dementia is a complex brain disorder that can be very tricky to diagnose, treat and manage. LBD is not as well-known as its cousin conditions, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, but it’s not a rare health problem. According to the National Institute on Aging, over 1 million Americans are affected by Lewy body dementia and its extremely challenging affects. (1)
Is there hope for people suffering from Lewy body dementia? Some LBD symptoms may respond to treatment for a period of time, but there’s currently no cure to Lewy body dementia. However, there is some good news. While having a family member with LBD can increase your risk, LBD is not normally considered a genetic disease, so just because it runs in your family doesn’t mean you’re destined to as well. More positive news — your lifestyle can have a big impact when it comes to your chances of developing brain diseases like Lewy body dementia. A healthy, nourishing diet, regular exercise and daily mental stimulation are just some of things you can do to help ward off and improve LBD. Read on to learn more about how to naturally treat and slow the progress of Lew body dementia.
Lewy Body Dementia Natural Treatment
1. Avoid Food Triggers
Diet plays a key role in cognitive decline and disorders like LBD or DLB. (2) Here are some foods to avoid to help prevent hte development of cognitive disorders.
- Sugar and refined carbohydrates — Eliminate unhealthy and concentrated sweeteners as well as refined carbohydrates. This helps stabilize your blood sugar and greatly reduce inflammation. Reducing sugar also encourages your brain to switch to more useful ketones for fuel. In addition, sugar and fat have been shown to induce cognitive decline when consumed in excess, which is why you want to greatly limit unhealthy sugars and fats in your diet. (3)
- Gluten — If you have an undiagnosed gluten intolerance symptoms or full-blown celiac disease, it could definitely affect you mentally. Nutritional deficiencies caused by celiac disease can exacerbate pathological processes in the brain causing memory loss, dementia and delirium. Gluten itself has also been linked to neurological problems. (4)
- Aluminum — Aluminum is toxic to the brain at high levels so avoid foods package in aluminum and also make sure you’re not using any aluminum-based cookware. Also avoid all aluminum-based deodorants. (5)
- Any food containing toxins or additives — These foods can possibly be neurotoxic. The best way to avoid toxins and additives is to completely avoid processed foods.
- Alcohol — Best to avoid alcohol all together since it can cause brain cells to die faster than normal. (6)
- Tap water — Tap water often contains environmental toxins, some of which could be damaging neurologically, so opt for purified water instead.
2. Eat Foods that Heal
To help Lewy body dementia, follow a low-carb diet that’s low in sugar yet nutrient-dense, high in good fats and loaded with anti-inflammatory foods. Healthy fats help mental disorders like Lewy body dementia because they facilitate proper thought-processing, hormone production and stress reduction mechanisms happening within the brain.
A ketogenic diet has been shown to be neuroprotective and very helpful for the dementia that comes with Lewy body dementia. (7) A ketogenic diet is made up of around 70 percent to 80 percent fat, which helps the brain. On this kind of diet, your body is able to burn fat for energy and utilize fatty acids, two critical things for the brain and for the natural treatment of dementia.
Here are the foods you should consume to help treat or prevent LBD.
- Organic, unprocessed foods — You want to eat foods that are free of harmful, brain-damaging, inflammatory pesticides and additives, but loaded with nutrients.
- Dark leafy greens — Consuming dark leafy greens like kale and collard greens can protect your brain from free radical damage. Green leafy vegetables and other foods rich in vitamin K, lutein and beta-carotene can help keep the brain healthy and preserve proper brain functioning.
- Berries — A great fruit choice for people with LBD, berries are low in sugar but high in anti-inflammatory antioxidants.
- Wild-caught fish — Great omega-3 foods, DHA specifically, fish are critical for brain health.
- Coconut oil — Coconut oil provides the brain with ketones that it can use instead of glucose. Some people have seen significant improvement in memory after adding coconut oil to their diets.
- Avocados & avocado oil — The good fat found in avocados can help lower depression and anxiety. Avocados and avocado oil are some of the richest sources of monounsaturated fats in the world.
- Ghee — Ghee’s levels of butyrate play a role in reducing inflammation in the digestive tract and throughout the body. In Ayurvedic practice, ghee benefits the body by creating a more alkaline system that overall reduces inflammation by reducing the leukotriene secretion and reducing prostaglandin in the body.
- Anti-inflammatory spices — Make a point to use anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric and ginger on a daily basis.
- Green tea — Green tea contains polyphenol antioxidants that help fight free radicals. It also contains theanine, which elevates dopamine levels in the brain and has a general calming effect. Try drinking three cups a day to reap the most benefits.
3. Take Beneficial Supplements
Melatonin is often used by Lewy body dementia patients to help with sleep problems. (8) Fiber supplements are also commonly taken and recommended if constipation is an issue. Probiotics can also help greatly when it comes to constipation and mood. (9)
For brain health, the following can also be helpful:
- Vitamin D3 (5,000 IU daily) — Vitamin D is required for brain function, and many of us (especially the elderly) are deficient in vitamin D because of the amount of time we spend indoors. (10)
- Ginkgo biloba (120 milligrams daily) — Helps improve brain circulation and memory and can be an effective natural treatment for dementia symptoms. (11)
The dementia aspect of Lewy body dementia symptoms is commonly much worse when a sufferer is frustrated, depressed, anxious or angry. Anything that’s successful at calming down the patient can be helpful to reduce and control Lewy body dementia symptoms.
4. Exercise
As usual, physical movement is a key part of fighting Lewy body dementia. Exercising regularly helps reduce depression and improve physical function. Research also shows that exercise can slow the progression of cognitive decline in people with dementia. Exercise may directly benefit brain cells by increasing blood and oxygen flow in the brain. (12) Yoga, tai chi and dancing are great choices for preserving balance and coordination. Physical activity is also a great way to prevent nighttime restlessness and encourage better sleep.
5. Pet Therapy
Assuming there are no allergies present, animal therapy can be excellent for LBD patients. Friendly dogs are often used to relax and bright up a patient’s day. (13)
6. Massage
What’s sure to lift a person’s mood and also help them to relax? Massage! Additionally, massage helps with circulation and detoxification. Even a brief rub of the shoulders can make a world of difference in reducing tension and keeping LBD symptoms at bay. (14)
7. Aromatherapy
The use of calming and uplifting essential oils like lavender, neroli and sweet orange can be very helpful. Frankincense oil and rosemary oil are also great choices for Lewy body dementia since they both support brain function and neurological health. You can use these oils in a diffuser. (15) You can also put two drops of frankincense oil on the roof of your mouth twice daily and rub rosemary oil into your scalp after a shower.
Listening to soothing music on a regular basis can help to reduce and calm symptoms of LBD. (16)
9. Daily Mental Stimulation
To prevent and slow the progress of any kind of dementia, it’s very helpful to find ways to stimulate the mind on a regular and daily basis. Doing crossword puzzles and playing games that use thinking skills are great options. This kind of daily mental stimulation can slow mental decline in people with dementia.
10. Peaceful Environment
It’s key that someone with Lewy body dementia has an environment that encourages a calm state. By reducing clutter and distracting noises, it can be easier for someone with LBD to focus and function. Clutter reduction can also decrease the risk for dangerous (or even deadly) falls and hallucinations. (17)
What Is Lewy Body Dementia?
Lewy body dementia is a progressive disease that involves having abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits are called Lewy bodies, and they affect chemicals in the brain. Those changes, in turn, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior and mood. LBD is one of the most common causes of dementia, after Alzheimer’s disease and vascular disease. (18)
There are two types of Lewy body dementia — dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. The early signs of these two types of LBD can be different, but they reflect the same biological brain changes. Dementia with Lewy bodies starts out with a decline in thinking ability that may look somewhat like Alzheimer’s disease. Parkinson’s disease dementia begins as a movement disorder with symptoms like slowed movement, muscle stiffness, tremors and a shuffling walk. As time goes on, someone with dementia with Lewy bodies and someone with Parkinson’s disease dementia tend to have similar LBD symptoms.
Lewy bodoy dementia is believed to be a “cousin” to Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease given the following facts: (19)
- Lewy bodies contain a protein associated with Parkinson’s disease.
- Lewy bodies often are present in the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.
- People who have Lewy bodies in their brains also have the plaques and tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The time span of having Lewy body dementia can range from two years to 20 years, but it typically lasts an average of five to seven years from the time of diagnosis to death. The development and progression of symptoms vary significantly from person to person, depending on overall health, age and severity of symptoms.
Lewy Body Dementia Symptoms
How can the presence of Lewy body dementia be recognized? The disease is especially challenging to diagnose due to its laundry list of symptoms that can vary on an individual basis. Early Lewy body dementia symptoms are commonly confused with similar symptoms found in other brain disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. LBD can occur alone or along with Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease.
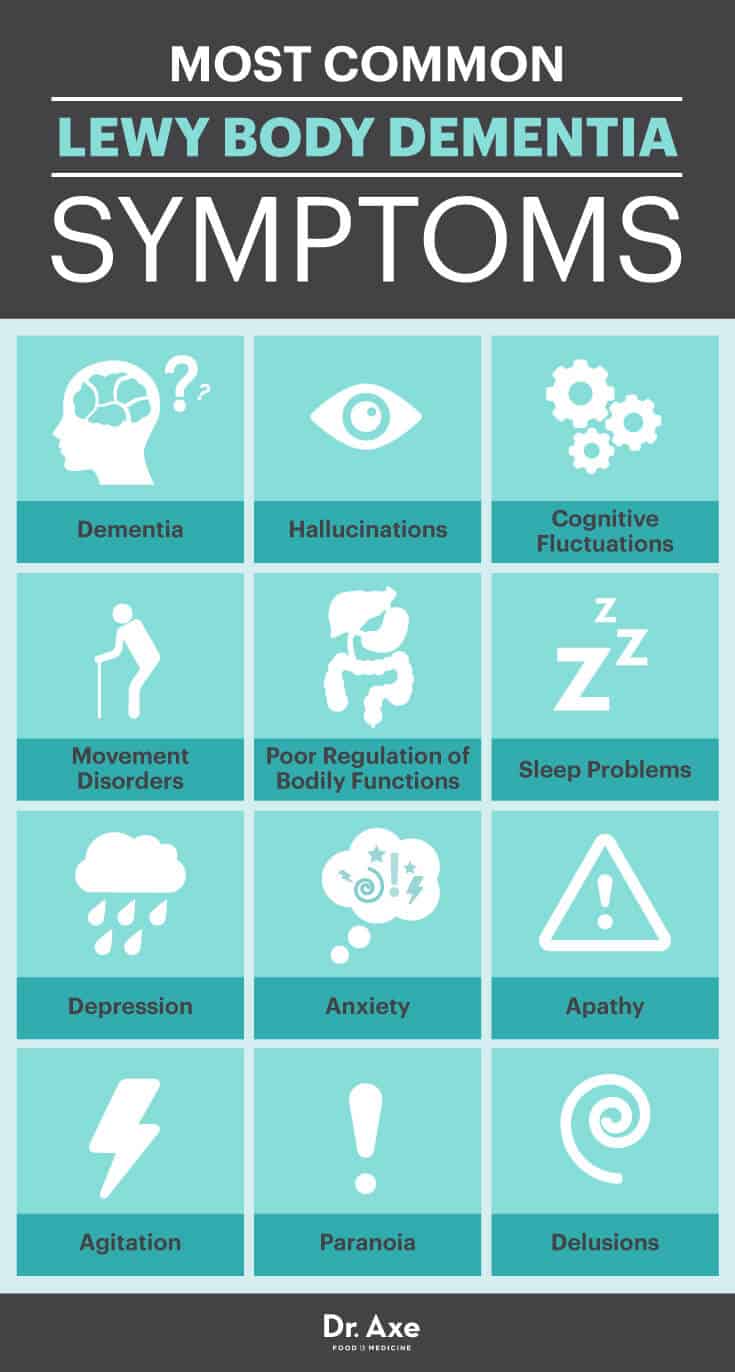
Common LBD Symptoms:
- Dementia — A group of symptoms negatively affecting memory, thinking and social abilities severely enough to interfere with a person’s daily functioning. Dementia is a primary symptom in LBD and usually includes trouble with visual and spatial abilities, planning, reasoning, multitasking, and problem solving. With LBD, sometimes memory issues are not evident at first but come about as the disease progresses. Dementia can also include changes in mood, behavior and judgment, as well as confusion about time and place and difficulty with language and numbers.
- Hallucinations — Seeing things that are not present is considered to be a visual hallucination. Visual hallucinations occur in up to 80 percent of people with LBD and often occur early on. They’re typically realistic and detailed, such as people, animals, colors or shapes that aren’t actually there. Auditory hallucinations are less common than visual ones but can also occur. Additionally, some people may also experience smell (olfactory) or touch (tactile) hallucinations.
- Cognitive fluctuations — Unpredictable changes in concentration, attention, alertness and wakefulness from day to day and/or throughout the day can occur. Someone with LBD may seem lethargic and drowsy, stare into space for lengths of time, or sleep for hours during the day even though he or she had adequate sleep the previous night. Flow of ideas may also be disorganized, unclear or illogical at times. Cognitive fluctuation in LBD patients can truly go up and down, appearing better one day, then worse the next.
- Movement disorders — LBD sufferers can experience symptoms similar to those of Parkinson’s disease or parkinsonian symptoms, including slowed movement, rigid muscles, tremors or a shuffling walk.
- Poor regulation of various body functions — Your blood pressure, pulse, sweating and digestive processes are regulated by a part of the nervous system that’s often affected by Lewy body dementia. Someone with LBD often experiences dizziness, falls and bowel issues.
- Sleep problems — Some people with LBD also have a sleep disorder called rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder that can cause someone to physically act out dreams while asleep. REM sleep behavior disorder appears in some people years before other LBD symptoms. People with LBD also often have insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness as well as restless leg syndrome.
- Depression — A persistent feeling of sadness, inability to enjoy daily life, trouble with sleeping, eating and other normal activities are signs of depression and also LBD symptoms.
- Anxiety — Intense apprehension or fear about future occurrences are common anxiety issues. Someone with LBD may ask the same questions repeatedly or be angry/fearful when a loved one is not present.
- Apathy — Lack of interest in normal daily activities and less social interaction can occur.
- Agitation — Easily restless or irritable, pacing, hand wringing, inability to get settled, and constant repeating of words or phrases are all signs of agitation that could be symptoms of LBD.
- Paranoia — Extreme, irrational distrust of others can take hold in those with LBD or DLB.
- Delusions — New, strongly held false beliefs or opinions not based on fact are considered delusions. Some LBD sufferers may have Capgras syndrome, in which the person believes a relative or friend has been replaced by an imposter.
Due to significant changes in the part of the nervous system that regulates automatic functions, such as those of the heart, glands and muscles, people with Lewy body dementia might also experience any of the following:
- blood pressure problems
- changes in body temperature
- constipation
- dizziness
- fainting
- frequent falls
- loss of bladder control
- poor sense of smell
- sensitivity to heat and cold
- sexual dysfunction
Lewy Body Dementia Root Causes & Risk Factors
The exact cause of Lewy body dementia is still unknown, but researchers continue to study and try to figure out this complex disease. We do know that an accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, or Lewy bodies, are associated with a loss of certain neurons that produce two important neurotransmitters, acetylcholine and dopamine. (20) Acetylcholine is key to the brain’s ability to remember and learn things while dopamine plays a crucial role in behavior, cognition, movement, motivation, mood and sleep.
Although the cause of Lewy body dementia isn’t clear, several factors appear to increase the risk of developing the disease. They include:
- Age — Being older than 50. Age is considered the greatest risk factor.
- Gender — Being male. Slightly more men than woman have LBD.
- Genetics — Having a family member with Lewy body dementia, but LBD is not normally considered a genetic disease. A small percentage of families with dementia with Lewy bodies has a genetic association with the disease. In some cases, it’s a variant of the GBA gene, but in most cases, the cause is unknown. Currently there is no genetic test that can accurately predict whether someone will develop LBD. (21)
- Other diseases — Having Parkinson’s disease or REM sleep behavior disorder is linked to a higher risk of LBD.
Final Thoughts
Many doctors are not familiar with Lewy body dementia so it might take going to several doctors before receiving a proper diagnosis. If you have a hard time finding a specialist nearby, ask the neurology department at your closest medical school for a recommendation. A hospital affiliated with a medical school is also a good place to receive an expert evaluation.
There is no single test that can diagnose Lewy body dementia so doctors often diagnosis the disease by process of elimination. Of course, if you have been diagnosed with Lewy body dementia, you should talk to your doctor before incorporating any natural supplements into your treatment plan, but you should also let your doctor know that you’re interested in what he or she knows about successful natural treatments for LBD. Some doctors won’t make recommendations for natural remedies unless it’s known that the patient has an interest.
Lewy body dementia is a very complex disease that poses great challenges for those that have it as well as their loved ones and caregivers. The good news is that there are many natural things that can be done by both the patient and caregiver to control LBD symptoms and improve quality of life. I’m hopeful that research and natural treatment options can continue to advance and improve the outlook for Lewy body dementia, and in the meantime, you can continue using diet and lifestyle to help prevent or treat cognitive disorders like LBD.
