This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
8 Deep Tissue Massage Benefits, Including Treating Chronic Back Pain
October 11, 2019
Whether you’re an athlete with a daily high demand placed on your body or recovering from an injury or illness, deep tissue massage likely has some benefits to offer you.
Massages have been utilized for thousands of years throughout the world to lower both physical and psychological stress. And today, research continues to show that whether used alone or in conjunction with other treatments, massage therapy is an effective way to help treat common conditions like arthritis, anxiety and chronic lower back pain.
Deep tissue massage benefits include reducing pain and discomfort, while improving the body’s ability to heal itself. Not only is this type of massages relaxing — studies show they also help “lengthen and release muscles” that frequently feel tense and get stuck in uncomfortable holding patterns.
Let’s explore what, exactly, deep tissue massage is and all the ways it can benefit your body and mind.
What Is Deep Tissue Massage?
Deep tissue massage, as defined by a 2018 article in the Journal of Bodywork And Movement Therapies, involves manipulation of the deep layers of muscle tissue in the body, including the fascia and other supportive tissue that make up joints. The purpose is to reach these layers in order to relax, lengthen and release harmful holding patterns.
Compared to other popular types of massage techniques — including Swedish massage or acupressure, which tend to be lighter in pressure and can involve moving the body into certain positions — deep tissue massage is usually performed more slowly and firmly.
Most deep tissue massages focus on major muscle groups — such as the neck or lower back — along with joints and tendons that are susceptible to straining or injuries. Certain areas of the body that tend to tense up in times of stress, including the shoulders, neck and hips, can often benefit the most from this type of deep manipulation.
Many people consider “sports massages” to be a form of deep tissue massage. These involve physical treatment primarily to neuromusculoskeletal systems to treat pain and disability, improve muscle recovery and joint mobilization, and prevent injuries.
Manipulative approaches to naturally treating pain and other health problems have been utilized for over 3,000 years, dating back to Ancient Egyptian and Chinese civilizations. Pressure massages were used to improve “Qi” (life force or energy), detox the body and promote better liver function — which today can be explained through the process of activating the lymphatic system.
Experts believe that the ancient Egyptians were the first to use very firm, deep pressure to treat chronic pain. In the West, deep tissue massage began to gain attention during the mid-19th century, starting in Canada and making its way throughout the U.S.
Benefits
What are the benefits of deep tissue massage? Below are some of the health conditions that this type of massage can help treat:
1. Treats Chronic Back Pain
One study that compared the effectiveness of two different kinds of massages for treating chronic back pain, therapeutic massage versus deep tissue massage (DTM), found that DTM treatment over the course of 10 days resulted in significantly better improvements in pain compared to therapeutic massage.
In this particular study, published in Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, therapeutic massage included techniques of tapping and friction, while DTM used “oblique pressure and a combination of lengthening and cross-fiber strokes.” All sessions were 30 minutes long and performed daily for 10days.
All participants did not receive any other treatments during the course of the study.
Other studies have show similar findings. A 2014 study published in the Scientific World Journal even found that DTM treatment alone had just as much of a positive effect on reducing pain in people with chronic symptoms compared to massage and NSAID painkillers used together.
A 2017 study found that various types of massage, including deep tissue, also seem to have clinical benefits for treating ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine.
(Gua sha therapy has also been found to help with lower back pain.)
2. Helps Lower High Blood Pressure
One study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that deep tissue massage had positive effects on systolic, diastolic and mean arterial blood pressure readings in adults with pain and high blood pressure symptoms.
The study involved 263 volunteers with an average age of 48.5. Overall muscle spasm/muscle strain was described as either moderate or severe for each patient prior to treatments, which consisted of a massage between 45–60 minutes in duration.
Results demonstrated an average systolic pressure reduction of 10.4 mm/Hg, a diastolic pressure reduction of 5.3 mm/Hg, a mean arterial pressure reduction of 7.0 mm/Hg and an average heart rate reduction of 10.8 beats per minute following massage treatment. Therefore, when looking for how to lower blood pressure, consider deep tissue massage therapy.
3. Reduces Stress, Anxiety and Muscle Tension
Why is massage good for people dealing with poor health due to stress? Mainly because it helps stimulate blood flow and relieve muscle tension, while at the same time lowering psychological stress and releasing “happy hormones” like serotonin and oxytocin.
Inflammation caused by chronic stress and muscle tension can lead to worsened overall health, longer recovery time, reduced immune function and cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure. Studies have found that massage therapy can help lower cortisol levels and even boost production of the hormone called oxytocin, which relaxes the body and has soothing effects.
Oxytocin is the primary hormone responsible for sustaining social bonds in humans and increasing motivation for cooperative behaviors, which is why it’s often called the “cuddle hormone” and known to be released during hugs, birth, social bonding and from touch.
Several mechanisms for deep massage’s natural stress-relieving effects include its ability to dilate blood vessels and also lower activity of the limbic system (including the hypothalamus), which is responsible for autonomic nervous system regulation and cortisol secretion.
Massage seems to improve relaxation by boosting activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, as measured by heart rate, blood pressure and heart rate variability.

4. Breaks Up Scar Tissue and Adhesions
Deep tissue massages are often utilized following injuries because research suggests massage help break up newly forming scar tissue that can make recovery more difficult and lead to stiffness.
Massage has been shown to help reduce inflammation and muscle spasms by stimulating blood flow, loosening up muscles to allow for more oxygen and also helping reduce the nervous system’s automatic stress response.
Following injury, and especially if it’s also a very stressful time, inflammation can prevent proper blood flow from reaching damaged tissue and can cut off vital nutrients and oxygen. This can cause toxins to accumulate around damaged tissue, which only increases swelling and pain.
Some studies have found that even self-administered massage along with icing can help reduce pain associated with plantar fasciitis and other common injuries. In this case, cross-friction massage strokes to the feet seem to be most effective for curbing pain.
5. Improves Athletic Recovery and Performance
Research published in the Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness reported findings of a positive trend for deep tissue massages in regard to improved athletic recovery and performance. The most beneficial type of deep tissue massage for athletes is considered to be “sports massage,” which is commonly performed prior to athletic events to help warm the body and prevent injuries or immediately after to improve recovery.
The report showed that the science of sports massage has become of growing interest to athletes, athletic trainers, coaches and sports physiologists. Studies show that deep tissue massages can help improve lactate clearance, delayed onset of muscle soreness, muscle fatigue, injury prevention and injury treatment.
The researchers also note there are psychological benefits for athletes receiving massages, which other research shows can include improved focus and confidence. Although more research is still needed on a long-term scale, both tissue healing and the psychological effects of massages are areas that seem promising for both professional and recreational athletes.
6. Can Help with Labor Pain and Delivery
Many pregnant women now turn toward alternative/complementary medicines for helping control labor pain and supporting a natural birthing process like the Bradley Method. In fact, surveys show that the most common alternative therapies recommended during pregnancy are massage therapy, acupuncture and chiropractic therapies.
Some research has shown that massage therapy can be effective during pregnancy due to its anxiety-lowering effects, and women who receive massages before and during labor tend to experience decreased depression, anxiety, and leg and back pain. Results from one study found that women who received massages prior to and during labor had significantly less pain, plus their labors were on average three hours shorter and required less need for medication.
Because cortisol levels decrease following massage and blood flow is improved, pregnant women are also better protected from excessive fetal activity and risk for premature delivery.
7. Reduces Arthritis Symptoms
According to the Arthritis Foundation, massage is often used to relieve common symptoms of many types of arthritis, including chronic joint pain, stiffness, anxiety, limited range of motion in joints and trouble sleeping. Firm massages can be used daily for natural relief, whether performed by a professional or by the patient themselves.
Research shows that firmer massages with more pressure can result in a significant reduction in arthritis pain compared to lighter massages, as well as tendonitis and similar types of painful conditions. Lighter massage tends to be arousing (not relaxing) because often the heart rate goes up.
However, with moderate pressure, heart rate usually goes down, and this stimulates relaxation and reduced tension.
8. Can Help Reduce Neck and Shoulder Pain
Surveys show that musculoskeletal disorders, particularly those affecting the shoulders and knees, are some of the most common health conditions that adults experience, impacting between 20 percent and 50 percent of the global population.
A 2015 study found that addition of soft tissue massage to an ongoing exercise program (in this case targeting the shoulder) offered additional benefits related to improvements in pain, disability and range of motion.
Findings from a 2017 review suggest that massage therapy is effective in improving shoulder flexion and abduction, as well as releasing “muscle hardness” that contributes to pain and reduced range of motion in the upper body.
According to an article written by the National Center of Complementary and Integrative Health, another 2013 review of 12 studies found evidence that massage was helpful for decreasing neck and shoulder pain. However, benefits were short-term in some of the studies.
A separate review found that massage could provide relief of neck pain most when treatments were frequent and long enough.
Related: Massage Gun Benefits, Best Types & Do They Really Work?
What to Expect and How It Compares to Other Massage
What happens when you get a deep tissue massage? The person receiving the massage usually lays on his or her stomach or back in one position, while deep pressure is applied to targeted areas of the body by a trained massage therapist.
Massage therapists who are trained in deep tissue massage technique usually offer their clients several services:
- They’re capable of safely treating particular areas that are extra tense or were previously injured.
- They can offer tips of improving posture, which can help lower chronic tension and pain.
- They usually have knowledge of helpful exercises or stretches that can be done at home between massage sessions.
- They also often have additional education in regard to reducing anxiety or stress held in the body and improving relaxation.
How often should you get a deep tissue massage?
Most experts recommend a maintenance plan of getting about one deep tissue massage per month. However, “the number of your appointments will vary if you have an acute injury, chronic pain or a more complicated condition.”
Athletes and those with injuries may want to undergo this type of massage more often, such as bi-weekly or once weekly.
Deep Tissue Massage vs. Swedish Massage
If you’ve ever received a massage that was done in a Swedish fashion — involving long strokes that moved along the lines of muscles — a deep tissue massage will probably feel like a bit of a different experience.
Deep tissue massages are usually “cross-grain,” moving against the muscles to relieve aches or pains rather than moving with them. This can sometimes feel a bit more painful as a result compared to standard “relaxation massages.”
However, the pressure involved in deep massages is actually a good thing. It provides many of the benefits that this type of therapeutic massage has to offer.
Deep tissue massages also tend to be slower-paced and longer than many other massages, ideally about 1.5 hours long, which gives bodily tissue enough time to warm up and then relax.
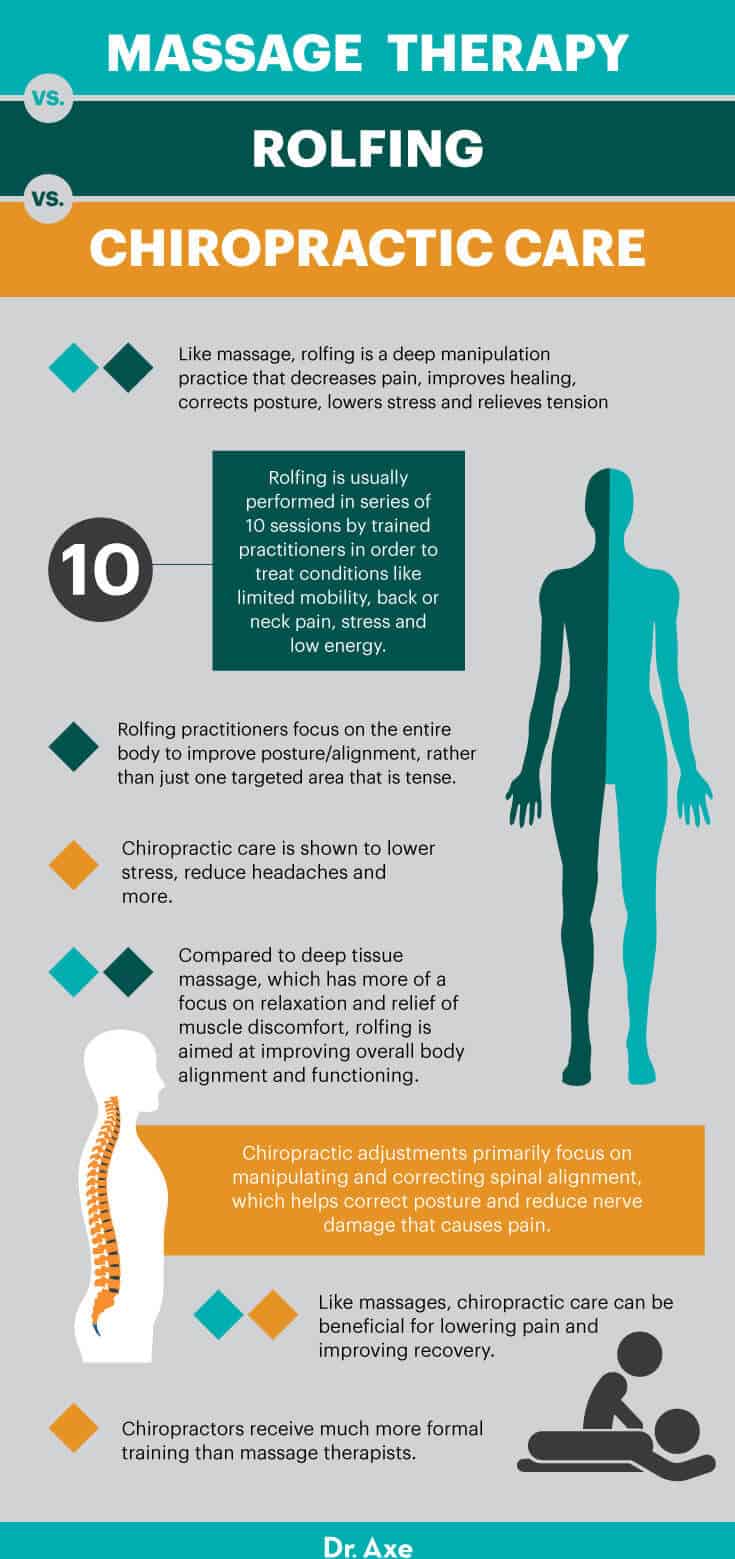
Massage Therapy vs. Rolfing
- Rolfing is one type of deep manipulation practice that has many of the same benefits of massages. It helps decrease pain, improve healing, correct posture, lower stress and relieve tension.
- Rolfing was founded in the 1950s by Dr. Ida Rolf, who created the practice to help treat damaged fascia, which are the bands or sheets of connective tissue fibers in the body that form beneath the skin to stabilize organs and muscles.
- Today, rolfing is usually performed in series of 10 sessions by trained practitioners in order to treat conditions like limited mobility, back or neck pain, stress, and low energy.
- According to Rolf USA, compared to deep tissue massage, which has more of a focus on relaxation and relief of muscle discomfort, “Rolfing is aimed at improving overall body alignment and functioning.” Rolfing practitioners focus on the entire body to improve posture/alignment, rather than just one targeted area that is tense.
Massage Therapy vs. Chiropractic Care
- Chiropractic care has some similarities to massage therapy but is also different. Chiropractic adjustments primarily focus on manipulating and correcting spinal alignment, which helps correct posture and reduce nerve damage that causes pain.
- Like massages, chiropractic care can be beneficial for lowering pain and improving recovery. It’s also been shown to lower stress, headaches and more. One way that chiropractors help treat pain is by lowering mechanical compression and irritation of spinal joints, which can send nerve signals throughout the body that increase inflammation and irritation.
- Compared to massage therapists, chiropractors receive much more formal training. They’re doctors who need four-year undergraduate education and also a four-year doctorate of chiropractic program. Many are also educated for years in nutrition therapy and various other healing modalities that lower psychological stress and improve immunity.
Risks and Side Effects
Deep tissue massages are not for everyone, and it’s very important to find a well-trained therapist to avoid any potential dangers.
If you’re actively healing from surgery, have nerve damage or an existing injury, you’re wearing a cast or brace, or you’re pregnant, then talk to your doctor before seeking a massage therapist.
Although it’s rare, deep tissue massage side effects may occur when a massage is poorly performed. This can sometimes cause increased pain, bruising, soreness, inflammation and other complications in high-risk patients.
How to Find a Massage Therapist
Do places like Massage Envy do deep tissue massages? It depends on the location and specific therapists who are employed there.
Although some massage therapists have a basic understanding of deep tissue massage, it’s best to find an accredited, well-trained therapist. This is especially the case if you plan to try neuromuscular therapy (NMT), which involves deep strokes that target delicate soft tissues around nerves.
According to the Neuromuscular Therapy Center, NMT is one type of deep massage technique that focuses on applying manual therapy to soft tissue with “quasi-static pressure” in order to stimulate skeletal striated muscle. In addition to massaging a painful or inflamed muscle, the area around the affected muscle that normally supports it is also massaged in order to release tension.
NMT therapists often focus on several factors that can add to muscle or tissue dysfunctions, including joint pathologies, postural positioning, disruptive habits of use, nutritional components, emotional well-being, allergies and neurotoxins.
- Certain massage therapists have specialized training in techniques that help treat people with injuries, inflammation, tears and limitations. Although more than one massage session is usually needed to provide relief and see improvements in pain, well-trained therapists can usually recommend practices or stretches for you to try at home that can further help improve healing.
- Requirements for massage therapists and regulations for licensing differ from state to state (and country to country). Typically, most licensed therapists need to graduate from an accredited massage therapy program and pass the MBLEx test.
- For specialized techniques like neuromuscular massage, keep in mind this can be more harmful than beneficial if done incorrectly, especially if you’re already injured and working on healing.
- It’s a good idea to mention your medical history, injuries and sensitive areas to your therapist before the massage begins.
- Many training programs are now available throughout the world that require a minimum of 500 hours of basic massage therapy training, in addition to continuing education credits that can require up to another 400–500 hours.
- Always make sure you’re “in good hands” by first checking that a therapist has proper qualifications and experience, specifically asking about training in NMT, trigger point therapy, sports massage, pain management, myofascial release and orthopedic massage.
Final Thoughts
- What is a deep tissue massage? This type of massage uses firm, manipulative pressure and movement to release deep layers of tissue, including tendons and fascia (the protective layer surrounding muscles, bones and joints).
- Deep tissue massage benefits include releasing chronic muscle tension, lowering spasms, treating anxiety, reducing arthritis symptoms, lowering blood pressure and improving recovery from injuries.
- Compared to Swedish massage or relaxation massage, deep tissue massage uses more pressure, is usually slower, and can last for a longer duration.


