This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Top 15 Vitamin E Foods & Their Benefits
December 21, 2022

From its potent antioxidant properties to its ability to protect your cells against damage, vitamin E can have a powerful effect when it comes to your health. Getting enough vitamin E foods in your diet may aid in the treatment of certain skin conditions, boost hair growth and even support healthy vision — in addition to the other vitamin E benefits these foods provide.
Found in a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds and oils, upping your intake of vitamin E is easy to do and can come with some pretty big benefits. Here’s what you need to know about this important micronutrient and how you can be sure to get in your daily dose.
Top 15 Vitamin E Foods
Getting enough vitamin E in your diet is crucial to overall health. Fortunately, vitamin E is abundant throughout the food supply, making it easy to meet your needs through your diet. It’s especially rich in many types of oils, nuts and seeds, as well as certain types of fruits and vegetables.
Not sure if you’re getting enough vitamin E foods in your diet? Take a look at some of the top sources on this vitamin E fruits and vegetables list and find out if it may be time to start upping your intake.
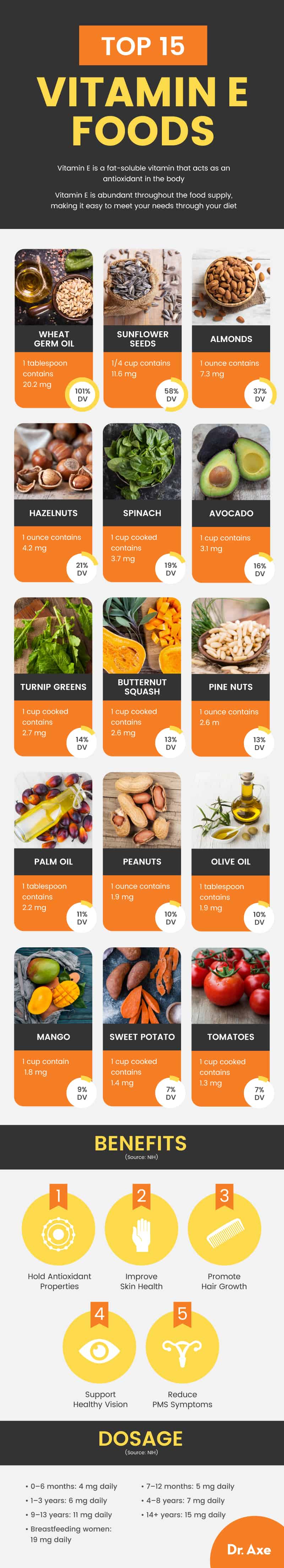
1. Wheat Germ Oil
One tablespoon of wheat germ oil contains roughly 20.2 milligrams (101 percent DV) of vitamin E. It also contains a host of antioxidants, which help wheat germ oil promote regularity, stabilize blood sugar, support heart health, manage weight and support immunity.
2. Sunflower Seeds
A quarter cup of sunflower seeds provides about 11.6 milligrams (58 percent DV) of this micronutrient. These seeds are also high in B vitamins, manganese and other minerals. As such, they can help lower the risk of heart disease, combat cancer, support the thyroid, protect bones and muscles, balance blood sugar, and promote skin health.
3. Almonds
One ounce of almonds holds approximately 7.3 milligrams (37 percent DV) of vitamin E. Almonds nutrition also supplies healthy fats, protein, and several other vitamins and minerals. Almonds are good for the heart, brain, skin, blood sugar, weight management, nutrient absorption, digestion, immune health, teeth and bones.
4. Hazelnuts
Supplying approximately 4.2 milligrams (21 percent DV) per ounce, hazelnuts have been shown to help promote heart health, manage diabetes, boost brain health, combat obesity and disease, and contribute to healthy nails and skin. Hazelnut nutrition is especially high in manganese, copper, magnesium and B vitamins as well.
5. Spinach
A cup of cooked spinach provides about 3.7 milligrams (19 percent DV) of this vitamin. Known for its high vitamin K content as well, spinach nutrition is an immune-boosting powerhouse that can defend against chronic disease, while supporting eye, bone, skin and brain health.
6. Avocado
With 3.1 milligrams (16 percent DV) in a cup, avocado benefits come from its tremendous nutrition profile, including its high vitamin E content. This superfood provides a healthy dose of good fats and just about every important micronutrient. That is why avocado is good for the heart, gut, skin, eyes, hair, brain, immune system and just about everything else.
7. Turnip Greens
Turnip greens nutrition provides 2.7 milligrams (14 percent DV) of vitamin E in one cooked up, as well as plenty of vitamins C, A and K, along with other micronutrients. These greens benefit the heart, bones, eyes and more.
8. Butternut Squash
There are about 2.6 milligrams (13 percent DV) of vitamin E in one cup of cooked butternut squash. Also high in antioxidants, butternut squash is good for combating inflammation, certain cancers, bone maladies and symptoms of PMS. It also can help with weight loss, physical performance and boosting energy.
9. Pine Nuts
Pine nut nutrition supplies roughly 2.6 milligrams (13 percent DV) of vitamin E in a one-ounce serving. Along with its other vitamins and minerals, pine nuts can help lower bad cholesterol, maintain healthy weight, reduce blood pressure, support bone health, improve eye health, stabilize mood and more.
10. Palm Oil
Cooking oils can be tricky, and while palm oil isn’t infallible, red palm oil does provide 2.2 milligrams (11 percent DV) of vitamin E in a tablespoon. As such, it can be beneficial in moderation, helping with cholesterol, brain and heart health, as well as skin and hair health.
11. Peanuts
So long as you aren’t allergic to peanuts, they can support metabolism and even aid fat loss when consumed with omega-3 foods. One ounce also contains 1.9 milligrams (10 percent DV) of vitamin E.
12. Olive Oil
One tablespoon of olive oil contains approximately 1.9 milligrams (10 percent DV) of this micronutrient. One of the healthiest oils around, olive oil benefits extend to the whole body, proving beneficial to the heart, waistline, brain and immune system. In fact, olive oil may help combat cancer, slow aging naturally and lower risk of diabetes.
13. Mango
Mango nutrition holds a good amount of vitamin E — about 1.8 milligrams (9 percent DV) in one cup — along with fiber and vitamins C, A, B6 and K. Like the other vitamin E foods mentioned, mango can help lower blood sugar, regulate blood pressure, boost brain health, protect against macular degeneration, support bones, optimize the heart, slow aging and more.
14. Sweet Potato
A cup of cooked sweet potatoes contains 1.4 milligrams (7 percent DV) of this vitamin. One of the healthiest potatoes available, sweet potato is high in antioxidants, providing an immune boost, along with being a healthy carb option.
15. Tomatoes
Tomato nutrition provides about 1.3 milligrams (7 percent DV) of vitamin E in one cooked cup. High in vitamins A, C and K as well, tomatoes are a versatile vitamin E foods that support the immune system, along with eye health and so much more.
What Does Vitamin E Do?
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that acts as an antioxidant in the body. It’s broken up into two different forms: tocopherols and tocotrienols. A specific form of vitamin E called alpha-tocopherol is the most commonly found form in the modern Western diet.
Because of its antioxidant properties, vitamin E is absolutely essential to health. Vitamin E benefits many aspects of health and has been shown to reduce PMS symptoms, support skin and hair health, and promote healthy vision.
It also protects your cells against oxidative damage, keeps your immune system running and helps prevent chronic disease. Plus, it reduces blood clotting and is involved in eye health, brain function and gene expression.
Because it’s so abundant throughout the diet, deficiencies are incredibly rare and usually only occur in people with other health conditions that impair the absorption of fat. However, a deficiency in vitamin E can come with some serious and long-lasting health consequences if not addressed.
Related: Vitamin E Oil for Skin & Hair
How Much Do You Need?
For most adults, it’s generally recommended to get in at least 15 milligrams of vitamin E daily, although this number jumps up to 19 milligrams for women who are breastfeeding.
The vitamin E requirement for children can vary widely based on age, however, as vitamin E needs gradually increase as we get older. Here are the recommendations for vitamin E intake from the National Institutes of Health:
- 0–6 months: 4 milligrams daily
- 7–12 months: 5 milligrams daily
- 1–3 years: 6 milligrams daily
- 4–8 years: 7 milligrams daily
- 9–13 years: 11 milligrams daily
- 14+ years: 15 milligrams daily

How to Add to Diet
Vitamin E can be found in a variety of foods that are available right at your local grocery store. To give your vitamin E intake a boost, simply head to the produce section, and start stocking up on a few foods with vitamin E, such as avocados, turnip greens, spinach and tomatoes.
You can also check out the health section of your favorite store or look online to find some of the more concentrated sources of vitamin E, such as wheat germ oil.
Vitamin E supplements are also available in capsule form and are often used by doctors to treat more severe vitamin E deficiencies. The gel from these capsules can also be extracted and applied directly to the hair or skin.
However, if taken by mouth, there is concern that vitamin E supplementation could increase the risk of bleeding and stroke. It may also cause side effects, such as stomach cramps, nausea, diarrhea and fatigue.
In most cases, it’s best to get your vitamin E through whole food sources rather than supplements unless under medical supervision to minimize the risk of these negative side effects. Not only that, but including a wide array of vitamin E-rich fruits and veggies in your diet can also supply other important nutrients that your body needs. In fact, many sources of vitamin E are also good sources of vitamin K and considered nutritious vitamin C foods as well.
Vitamin E Foods Recipes
Making a few simple switches to your diet is the best way to squeeze in extra servings of vitamin E foods. There are plenty of nutritious (and delicious) foods rich in vitamin E to choose from, making it easier than ever to increase your intake.
Here are a few recipes that pack in a hearty dose of vitamin E to help you meet your daily needs:
- Avocado Grilled Cheese
- Sweet Potato, Chickpea and Spinach Coconut Curry
- Mango Coconut Ice Cream
- Sauteed Turnip Greens with Pine Nuts and Raisins
- Butternut Squash Soup
Conclusion
- Vitamin E is a type of fat-soluble vitamin with antioxidant properties. In addition to reducing oxidative stress and blocking blood clotting, it’s also involved in eye health, brain function and gene expression.
- It’s found in abundance throughout many different foods, but some of the best sources of vitamin E include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds and oils.
- In addition to acting as an antioxidant, vitamin E may also help reduce PMS symptoms, promote hair growth, support better vision and improve skin health.
- Deficiency in vitamin E is rare and usually only occurs alongside other health conditions that impair fat absorption. Vitamin E deficiency symptoms can include muscle pain, weakness, vision problems and numbness.
- Although supplements are available, there is some concern that they may come with adverse side effects. Instead, it’s best to incorporate a wide variety of vitamin E foods in your diet to help meet your micronutrient needs.


