This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
How to Get Rid of Hiccups: Try These Natural Remedies
June 3, 2021

Having the hiccups is a mysterious occurrence, and just about everyone wonders how to get rid of hiccups. Unlike other common reflexes, like sneezing and coughing, there’s no known physiologic advantage for the hiccups.
Yet, we’ve all experienced them numerous times in our lives. Every one has her own suggestion for how to get rid of hiccups, but what really works?
Sometimes hiccups occur because the nerves that run from your brain through your lungs and stomach are irritated and cause a sudden spasm. Hiccups can also be due to acid reflux or GERD, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease. Certain medications can cause them as well.
For the most part, they go away on their own after a short period of time. However, in some situations hiccups can last for months or even years.
Whether you are trying to get rid of acute hiccups because they are bothersome or you are suffering from long-term hiccups, there are natural remedies that can help. Read on to find out how to get rid of hiccups for good and when it may be a good time to see a doctor.
What Are Hiccups?
Hiccups are reflexes that cause a sudden contraction of your diaphragm, the primary muscle that’s under your lungs and used in the process of inhalation. After it involuntarily contracts, air abruptly rushes into the lungs and is stopped suddenly by the closure of the vocal cords, or glottis. This is what causes the “hic” sound.
Research published in the Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine shows that a hiccup, referred to in medicine as singultus, is a programmed muscle exercise. We know this because fetuses and premature infants hiccup often. After infancy, hiccuping appears to be useless, but it may occur because of an irritation along the reflex arc.
A hiccup occurs when the vagus nerve and the phrenic nerve send strong signals from the brain stem to the respiratory muscles. The external intercostal muscles (which run between the ribs and help with breathing) and the diaphragm contract and cause a forceful inhalation.
When you hiccup, you may feel a slight tightening sensation in your throat, chest or abdomen. The major sign of a hiccup is the “hic” sound that occurs when your windpipe closes immediately after your diaphragm contracts.
Everyone’s hiccup rate is different, but it’s usually consistent for each hiccup episode, occurring at a frequency of four to 60 hiccups per minute.
Hiccups are said to be persistent when they last longer than 48 hours. When that happens, they can affect food and drink intake, conversation, and concentration.
Studies indicate that this can lead to complications like exhaustion, frustration, insomnia and even potentially fatal consequences, like aspiration pneumonia.

Causes
For most people, hiccups last for a short period and then stop. They can happen at any time, and sometimes they start for no apparent reason at all.
They can also be due to following causes:
- a swollen stomach caused by eating too quickly or overeating
- swallowing air
- drinking carbonated beverages
- sudden excitement
- sudden emotional stress
- consumption of alcohol
- excess smoking
- a sudden change in stomach temperature
In the short term, acute hiccups are most prevalent in newborns, who spend as much as 2.5 percent of their time hiccuping. Reports show that after infancy, the frequency of hiccups diminishes and only happens occasionally for brief periods throughout life.
Hiccups that last longer than 48 hours may be due to a variety of factors. Researchers suggest that these can include the following health issues or triggers:
- gastrointestinal issues
- central nervous system disorders
- metabolic disorders
- psychogenic disorders
- certain medications
The two nerves that are involved in this involuntary contraction are the vagus and phrenic nerves. The vagus is the longest cranial nerve that contains motor and sensory fibers. It exits from the brain and passes through the neck and thorax to the abdomen.
The phrenic nerve originates in the neck and passes down between the lung and heart to reach the diaphragm. The phrenic nerve stimulates the diaphragm, so it’s known that paralysis to this nerve can lead to persistent hiccups.
For some people, ongoing hiccups are due to GI issues, like acid reflux, bloating and heartburn, which can irritate the diaphragm.
Long-term hiccups may occur because of lesions between the pathway from the central nervous system to the phrenic nerve. This occurs mainly in diseases of the brain stem, such as stroke, tumors, meningitis, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis and traumatic brain injury.
Metabolic problems may also lead to persistent hiccups. They can be a sign of worsening kidney or liver function, for instance.
Research published in the Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine referenced above shows that long-term hiccups are more common in children, adult men and those with comorbid conditions.
How to Get Rid of Hiccups
You’ve probably heard of numerous home remedies on how to get rid of hiccups. What exactly are you trying to accomplish with these methods? Most of these treatments are meant to reset the vagus nerve or allow your body to relax.
One particular action may not stop your hiccups every time, so you may have to try a few of these home remedies until you find what works.
1. Stimulate the Vagus Nerve
The vagus runs from your brain to your stomach. Researchers believe that irritation to this nerve can cause hiccups, so you can try these simple actions to “reset” it so they disappear.
You can “irritate” the pharynx and thereby stimulate the vagus by sipping a glass of cold water, chewing on a lemon or eating a spoonful of raw honey mixed with water.
2. Relax Your Diaphragm
Another goal is to relax the diaphragm and stop the spasms or contractions that cause hiccups from happening. One way to do this is to make the body retain carbon dioxide, which can be done by holding your breath for 10 seconds at a time or breathing into a paper bag.
Breathing into a paper bag increases the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood and makes the diaphragm contract more deeply in order to bring in more oxygen. Reports indicate that this usually helps and is an effective way for how to get rid of hiccups.
Take deep breaths into a small paper bag, but stop if you begin to feel lightheaded.
3. Pull Your Knees to Your Chest
Pulling your knees to your chest compresses your chest, which serves as a counter-irritation and may help stop the contractions that cause hiccups. You can also try leaning forward to compress your chest.
Take deep breaths in and out as you compress your chest and try to reset the signals that cause spasms.
4. Try the Valsalva Maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is when you blow air out of your lungs while blocking your mouth and nose. This technique is used to increase the pressure in the throat, sinuses and inner ear.
Research reveals that some people use this breathing technique to stop an arrhythmia because it works to reset signals within the body.
To do the Valsalva maneuver, breathe out forcefully for 10–15 seconds as you keep your mouth closed, and pinch your nose. The pressure this puts on your nasal sinuses helps alleviate hiccups.
5. Use Peppermint Oil
Peppermint essential oil can be used to get rid of hiccups because it stimulates belching by relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter. By placing one drop on the roof of your mouth, you can help stop the contractions that lead to them.
Dilute peppermint oil with coconut or grapeseed oil before ingesting it.
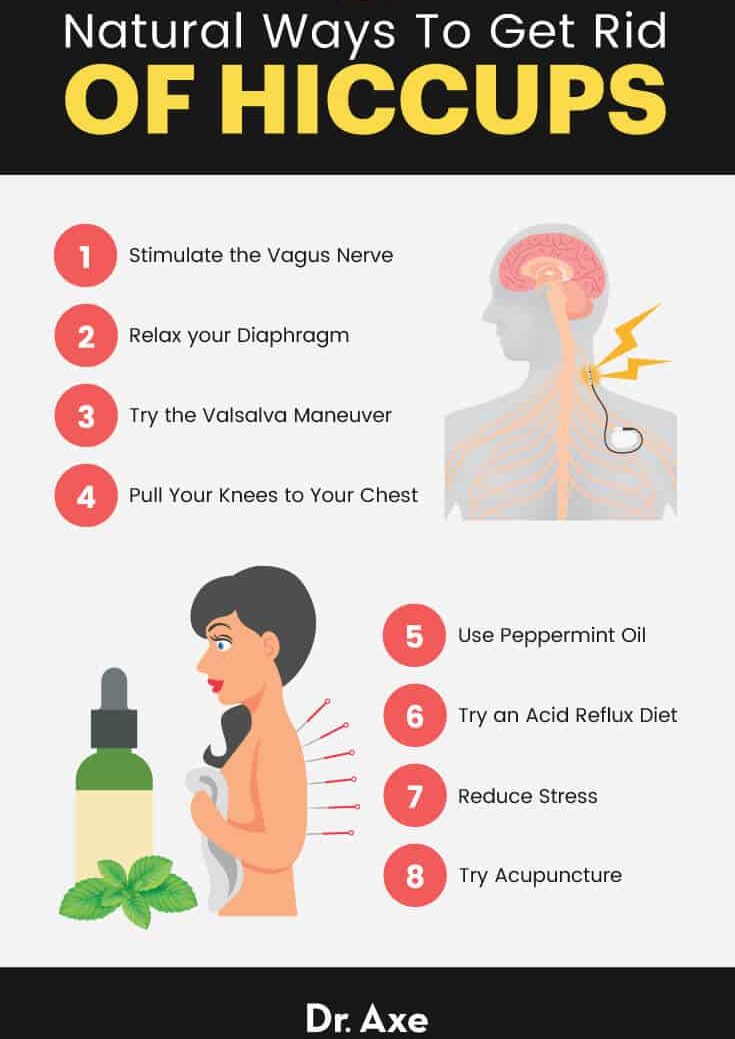
6. Try an Acid Reflux Diet
Persistent hiccups can be a common acid reflux symptom. Aside from them, you may experience heartburn, a bitter taste in your mouth, dry mouth, bad breath, burping and flatulence.
Virtually every study done on GERD and acid reflux points to diet as a contributing factor.
Research states that your body is trying to alert you to a problem in your digestive tract. You should also work on slowing down while you eat, chewing your food well and eating smaller meals throughout the day instead of three large meals.
Wondering how to get rid of hiccups by reducing your acid reflux? Do the following:
- Stick to unprocessed, organic foods that are free from GMOs as much as possible.
- Increase your fiber intake to support healthy bacteria in your gut, and eat plenty of probiotic foods.
- Reduce grains, especially when refined, and sugar consumption, and eat high-quality protein. (Stick to grass-fed beef over conventional beef.)
- Reduce your intake of refined vegetable oils, like canola oil.
Some people also find that carbonated drinks, alcohol and spicy foods can lead to hiccups, so do your best to minimize those foods and drinks in your diet.
Eat the following foods to get rid of hiccups that are due to acid reflux:
- leafy greens
- squash
- artichoke
- asparagus
- cucumbers
- watermelon
- honeydew
- bananas
- free-range chicken
- grass-fed beef
- avocado
- yogurt
- kefir
- bone broth
- coconut oil
- olive oil
- apple cider vinegar
- aloe vera
- ginger
- fennel
- parsley
7. Reduce Stress
Stress is one of the most common causes of short-term hiccups. Next time you get the hiccups, think about how you’re feeling in that moment and whether or not stress may be playing a role in the development of them.
If that’s possible, then practice some simple stress relievers every day. These could include:
- exercising or practicing yoga
- trying meditation or healing prayer
- spending more time in nature
- using stress-reducing essential oils, like lavender and Roman chamomile
8. Try Acupuncture
Case studies show that acupuncture may effectively treat persistent hiccups, even when conventional forms of treatment don’t work. Acupuncture is used to stimulate or irritate the nerves that are responsible for them.
Although there are no controlled studies involving acupuncture and hiccups, some people have been able to cease their long-term hiccups with this form of treatment, so it may be worth a try.
9. Conventional Medications
Most of the time, hiccups go away on their own after a relatively short period of time, and medical treatment from a doctor isn’t necessary. People who have them for longer than two days may need to address the underlying medical issue that causes them.
Some conventional medications that are used to treat long-term hiccups include:
- Chlorpromazine (or Haloperidol): Chlorpromazine is used to relieve prolonged hiccups, control nausea and vomiting, and treat behavioral problems or anxiety disorders. This is typically the first medication prescribed to people suffering from long-term hiccups. Some side effects from this drug include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, constipation and trouble sleeping.
- Gabapentin: Gabapentin is usually used to prevent and control seizures. It is an anticonvulsant drug, which is why it can be used for the treatment of long-term hiccups. It may cause tremors, dizziness and loss of coordination.
- Metoclopramide: Metoclopramide increases muscle contractions in the upper digestive tract, and it’s used to treat heartburn caused by GERD, one of the most common causes of hiccups. High doses or long-term use of this drug can be toxic, leading to serious movement disorders. If you take this drug, make sure to speak to your doctor about the many medicines that interact with it. These include vitamins and herbal products.
- Baclofen: Baclofen is used to treat muscle spasms that are caused by conditions like multiple sclerosis and a spinal cord injury. Side effects from this drug include headache, weakness, nausea and trouble sleeping.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are used to treat gastroesophageal reflux, which promotes hiccup formation. Taking PPIs may lead to increased gas, abdominal pain, digestive issues and headache.
Getting Rid of Hiccups in Newborns
It is common for newborns to get hiccups, and usually they don’t bother them as much as they bother adults. To prevent hiccups in your baby, try to burp him or her throughout a feeding. Burping gets rid of excess gas that may cause hiccups.
It can also help to feed the newborn when she’s calm and let her digest in an upright position for at least 20 minutes before she engages in heavy activity, like bouncing up and down.
Wondering how to get rid of hiccups in your baby? Try changing her position, burping the baby or calming the baby. Giving your baby a pacifier may help relax her diaphragm and stop the hiccups.
If 10 minutes have passed and the baby still has hiccups, try feeding her from the breast or a bottle. This sometimes can be how to get rid of hiccups in a baby.
When to See a Doctor
Hiccups typically last a few minutes or even hours. If they don’t go away within two days, it’s time to speak to your doctor and learn about what may be triggering ongoing hiccups.
There’s no one cure for them, but your health care provider can determine if they are caused by an underlying condition and provides ways for how to get rid of hiccups.
Risks and Side Effects
If your hiccups are so severe that they make it difficult for you to breathe, sleep or eat, or if they last longer than two days, then consult your health care provider.
If your doctor determines that conventional medicine is needed for long-term hiccups, discuss potential interactions with vitamins or supplements.
The natural ways to reduce hiccups listed above are generally safe, but if you begin feeling lightheaded or experience any discomfort, stop using that remedy.
Final Thoughts
- Hiccups are reflexes that cause a sudden contraction that effects your respiratory muscles, and many people wonder how to get rid of hiccups naturally.
- When you hiccup, you may feel a slight tightening sensation in your throat, chest or abdomen. The major sign of a hiccup is the “hic” sound that occurs when your windpipe closes right after a contraction.
- Acute hiccups can be caused by overeating, drinking carbonated beverages, drinking alcohol, smoking, sudden excitement, emotional stress, swallowing air or sudden changes in stomach temperature.
- Long-term hiccups (lasting longer than 48 hours) can be caused by gastrointestinal issues, central nervous system disorders, metabolic disorder, psychogenic disorders or certain medications.
- Wonder how to get rid of hiccups? There are a number of ways to stop them, including drinking a glass of water, trying to hold your breath and relieving stress.
