This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Improve Your Homocysteine Levels to Protect Your Heart
September 23, 2016

Never heard of homocysteine before and wondering what causes someone to have elevated homocysteine levels?
Homocysteine is a specific type of amino acid that’s created in the body during metabolic processes, as opposed to consumed in food. It’s produced in the body as a byproduct of methylation, the process of producing an essential protein called methionine. In healthy people, homocysteine is transformed into a benign product that keeps levels maintained, but when homocysteine isn’t properly metabolized it builds up inside the body and acts similarly to a toxin. This causes inflammation to rise and creates more byproducts that cause changes in cardiovascular, neurological and endocrine systems.
High homocysteine is a common cause of inflammation of the arteries and therefore tied to heart disease. (1) Heart disease is a leading cause of death, and some research suggests that about 15 percent of all heart attacks and strokes might be tied to high homocysteine levels. (2) Starting around the 1960s, doctors uncovered that genetically inherited high homocysteine levels were the cause of fatal heart problems in certain children, and this encouraged researchers to investigate links between elevated homocysteine and cardiovascular diseases in adults too. (3)
Disorders that cause abnormal homocysteine levels can contribute to a wide range of other health problems and symptoms too — such as decreased vision, fatigue or depression, and skeletal abnormalities in children among some of the most common. Although it’s not always possible to “cure” abnormal homocysteine levels, due to the condition commonly being caused by a genetic inheritance, natural ways to help manage the symptoms it causes include eating an anti-inflammatory diet, reducing stress, supplementing to reduce deficiencies and staying active.
What Is Homocysteine?
As mentioned above, homocysteine is an amino acid that’s normally not dangerous or unhealthy, until it accumulates to high levels. Homocystinuria is the name of the condition that’s characterized by high homocysteine levels due to a lack of the enzymes that normally metabolize homocysteine. This metabolic disorder is sometimes referred to as an enzyme defect, which is normally genetic and passed down from parents to their children.
Homocysteine levels are also maintained through the presence of certain vitamins and production of enzyme cofactors. This is why deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate and vitamin B6 can contribute to homocysteine problems.
Elevated homocysteine is seen in both children and adults. Children with homocystinuria usually inherited a specific type of genetic MTHFR mutation that interferes with normal enzyme production and a process called methylation. (4) Children can start developing symptoms at a young age, although sometimes adults with unhealthy lifestyles are also diagnosed with high homocysteine levels for the first time.
Symptoms of High Homocysteine Levels
Symptoms of elevated homocysteine levels can be either mild or severe depending on which types of enzymes and nutrients someone is lacking. Most infants with homocystinuria are usually born normal and healthy until symptoms start to emerge around the age of 3. Some of the earliest signs of abnormal homocysteine levels? These can include vision changes (due to dislocation of the lens) and postural problems (due to skeletal abnormalities and the gradual development of osteoporosis).
Many adults develop high homocysteine at a later age, most without even knowing it at the time. Although symptoms aren’t always present, here is a more robust list of common signs or complications caused by having high homocysteine: (5)
- Higher risk for heart problems, such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, stroke, high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels — this is due to increased inflammation, sometimes due to blood clotting spontaneously and also because of blockages of the major arteries
- Greater risk for Alzheimer’s disease, dementia and other cognitive problems
- In children, skeletal and developmental abnormalities — this can include having a curved spine or protruding chest and rib cage
- Elongated limbs and extremities — some patients appear very tall and thin, and some might also have very long, thin, “spider-like” toes and fingers
- Behavioral problems, including ADHD, autism and other learning disabilities
- Migraines and headaches
- Mental abnormalities — depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder and other mental problems are more common among people with high homocysteine
- In those who suffer from high homocysteine due to having nutritional deficiencies, anemia, aches and pains, slowed development, and birth defects might also be possible
Causes and Risk Factors of Elevated Homocysteine Levels
One genetic cause of high homocysteine levels is being born with an MTHFR mutation. (6)
- An MTHFR gene mutation can change the way some people metabolize and convert important nutrients from their diets into active vitamins, minerals and proteins.
- It’s believed that up to 30 percent to 50 percent of all people might carry a genetic MTHFR mutation and around 10 percent to 20 percent of the population might have more severe MTHFR mutations.
- The MTHFR genes produce enzymes that convert homocysteine into another amino acid called methionine. The less enzymes created, the more dramatically someone’s health is impacted, since this can significantly raise homocysteine and therefore inflammation levels.
- Some people with these mutations produce up to 70 percent to 90 percent fewer enzymes needed to break down homocysteine than those without MTHFR mutations. Other experience much less drastic drops in enzyme levels, around 10 percent to 30 percent.
Another reason that homocysteine levels become elevated in adults without genetic enzyme mutations is that they’re suffering from nutritional deficiencies, including those of folate and B vitamins (especially vitamin B6 and vitamin B12). Research has shown that supplementing with these nutrients can help reduce someone’s risk of inflammatory heart conditions, cognitive decline, depression and more since it helps decrease the amount of homocysteine in the blood. (7)
Other than simply not eating enough foods with these nutrients, what puts someone at an elevated risk for folate deficiency or being too low in B vitamins? Studies show that homocysteine levels tend to rise with age, smoking and use of certain drugs, so the first step is to focus on taking care of yourself of as you get older and limiting use of harmful substances. Men also tend to have higher levels.
People who are more likely to run low in these essential nutrients that are tied to high homocysteine levels include:
- Pregnant women or breast-feeding mothers
- Alcoholics and drug users
- Anyone with liver disease
- Anyone on kidney dialysis
- People with diabetes, thyroid disorders or hormone imbalances
- Those frequently using diuretics or laxatives
- Anyone taking medications that can further deplete already low folate levels or interfere with methylation. These include diabetes drugs, high cholesterol drugs, antibiotics, birth control pills, anticonvulsants (like phenytoin and carbamazepine), antacids, NSAID pain relievers and antidepressants
Natural Treatments for High Homocysteine Levels
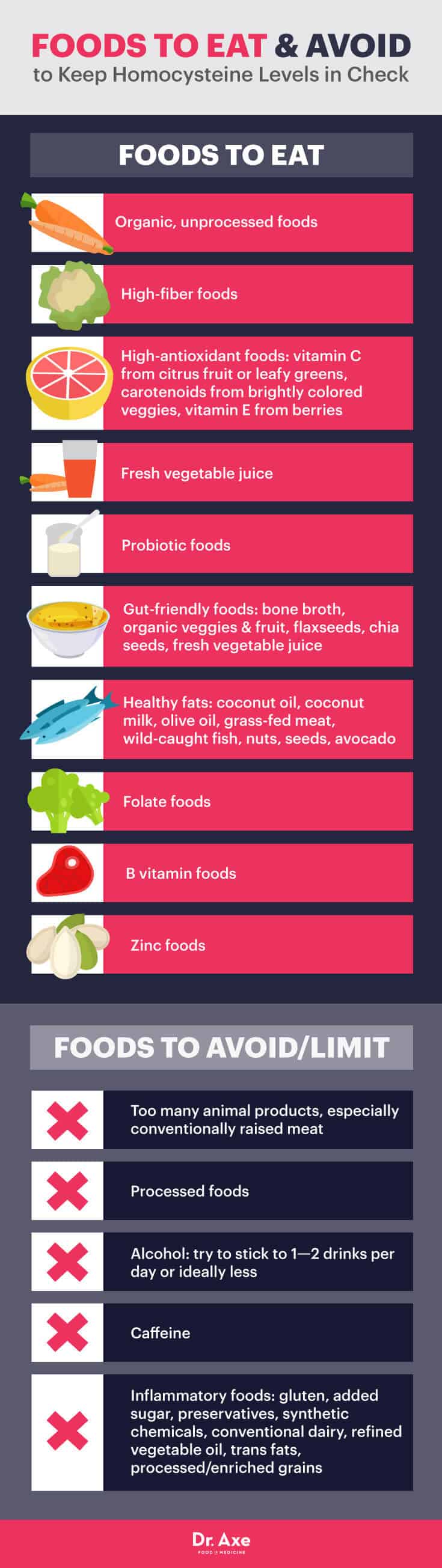
1. Improve Your Diet
Your diet can make a big impact on the severity and frequency of symptoms you experience as a side effect of having high homocysteine levels. If you consume a lot of animal products (especially the kinds that are conventionally raised and not grass-fed) and processed foods, you’re more likely to have high homocysteine.
Here are dietary tips for protecting yourself from high homocysteine complications (including heart disease, neurological problems, chronic pain and mood disorders).
Eat Mostly Organic, Unprocessed Foods
High homocysteine not only increases inflammation, but also makes it harder for the body to detoxify itself of built-up chemicals, heavy metals and toxins. Because processed foods and those containing pesticides commonly contain many synthetic chemical ingredients, it’s beneficial to avoid eating these as much as possible.
Consume More Fiber
Fiber helps protect your arteries and heart, improves digestion, can help regulate your appetite, lowers overeating, and is even tied to healthier cognitive functioning.
Get Plenty of Antioxidants
These include vitamin C from citrus fruits or leafy greens, carotenoids from brightly colored veggies, and vitamin E from things like berries. Drinking fresh vegetables juice is a great way to increase your antioxidant intake every day.
Limit Your Alcohol and Caffeine Intake
Only consume alcohol in very small amounts, roughly one to two drinks per day or ideally less. Caffeine is also tied to higher homocysteine, so try cutting back or eliminating your consumption.
Reduce Intake of Inflammatory Foods
Avoid foods like gluten, added sugar, preservatives, synthetic chemicals, processed meats, conventional dairy, refined vegetable oils, trans fats and processed/enriched grains (which often include synthetic folic acid).
Increase Intake of Probiotic Foods
Probiotic foods are fermented and supply “good bacteria” that help control leaky gut syndrome and inflammation. Also consume other gut-friendly foods, including bone broth, organic vegetables and fruit, flaxseeds and chia seeds, and fresh vegetable juices.
Focus on Consuming Healthy Fats Only
Healthy fats include coconut oil or milk, olive oil, grass-fed meat, wild-caught fish, nuts, seeds, and avocado.
Get More Natural Folate, B Vitamins and Zinc
There’s more on this below.
2. Get Enough Folate (Vitamin B9)
Many people don’t get enough natural folate in their diets, which can contribute to not only high homocysteine, but also problems like digestive complaints, neurological decline, anemia, fatigue, skin sores and even birth defects in pregnant women. (8) Research has shown that by increasing your intake of natural or activated folate (not the same as folic acid), you can reduce your risk for problems related to high inflammation levels. Foods that are high in folate include beans, legumes, broccoli, spinach and leafy greens, organ meats like liver, ancient grains, poultry, and avocado.
Why is it best to avoid folic acid and get your folate the natural way instead? Folic acid is a synthetic B vitamin found in supplements and fortified foods (like processed grains or orange juice). Real folate is directly metabolized by the small intestines, but synthetic folic acid requires the assistance of a specific enzyme called “dihydrofolate reductase,” which is usually only present in the body in small amounts.
It’s estimated that about 35 percent of adults and 28 percent of all children in the United States use supplements containing folic acid. Unmetabolized folic acid can remain in the bloodstream and contribute to certain health problems, possibly including cancer. (9) On the other hand, it appears that eating a balanced diet with plenty of veggies and plant foods might have the opposite effect — offering protection from things like heart disease and depression.
3. Consume More Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B12
Many patients with high homocysteine experience improvements in symptoms when they consume more B vitamins, especially vitamin B6 and B12. These help increase metabolic functions, including methylation, and can lower symptoms, such as cognitive dysfunction and fatigue.
Vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 benefit the body in many ways, including helping with nutrient absorption, energy expenditure and brain function. (10) Folate also helps vitamin B12 to be absorbed properly, so some experts recommend consuming these two nutrients together. However, there is also concern that high folic acid intake from supplements might “mask” vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms and make neurological consequences even worse down the road. Just another reason to avoid supplementing with large doses of synthetic vitamins and to get nutrients the natural way.
What foods help you consume more B vitamins? Focus on eating enough quality protein foods, pasture-raised poultry, organ meats, nuts, beans, nutritional yeast and raw/fermented dairy products. These same sources also supply zinc and other amino acids, which further help with methylation.
4. Protect Your Heart
People with metabolic disorders that affect homocysteine levels and contribute to inflammation plus plaque formation are at an increased risk for developing coronary heart disease (also called atherosclerosis) and other disorders. Because of this, it’s crucial to mitigate other risk factors for heart disease, including smoking, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, diabetes and a poor diet that increases inflammation. Focus on eating a healthy diet, especially one with plenty of high-fiber foods, getting regular exercise and keeping your weight in a healthy range.
If you have high homocysteine and an increased risk for heart problems, it’s also beneficial to consume supplements that can help improve blood flow, cholesterol and blood pressure. These include magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, Coenzyme Q10, carotenoids and other antioxidants, selenium, and vitamins C, D and E.
5. Exercise Regularly Into Older Age
Regularly exercising helps mitigate problems caused by high homocysteine by improving immune function, hormonal balance, stress levels, sleep quality, body weight control and inflammation. Find a form of exercise you enjoy and can stick with, whether it’s lifting weights, dancing, yoga, running, cycling or swimming.
6. Get Enough Rest and Manage Stress
The same health conditions and lifestyle habits that raise homocysteine levels can also cause increased anxiety, insomnia, fatigue and depression. One of the reasons this is true is due to the effects that enzyme defects and nutrient deficiencies have on levels of neurotransmitters and hormones — like serotonin, testosterone and estrogen. These hormones govern things like sleep, sex drive, motivation and energy levels. All of these problems are also made worse by high amounts of day-to-day stress.
Tips for dealing with these mood-related conditions include:
- Regularly practicing natural stress relievers, including exercising, meditation, journaling, spending time outside, giving back or volunteering, praying, etc.
- Using essential oils for anxiety or stress, including lavender, chamomile, geranium, clary sage and rose.
- Eliminating use of recreational drugs and reducing alcohol intake, which can both make symptoms worse by interfering with methylation.
- Improving quality of sleep (aim for seven to nine hours nightly) by practicing a relaxing bedtime routine, staying off of electronic devices, reading something soothing and making your bedroom dark and cool.
Precautions When Treating Abnormal Homocysteine Levels
High homocysteine is not always easy to spot, so keep up with doctor appointments and ask for specific testing if you suspect a problem.
Wondering how high homocysteine is diagnosed?
Since 2008, almost every state in the U.S. has been required to screen newborns for abnormal homocysteine levels, given the fact that early diagnoses and treatment can make a huge impact on mitigating long-term effects. (11) In adults, homocysteine tests are usually performed through blood tests. Sometimes skin cell tests or enzyme and liver function tests are also performed to assess a patient’s ability to metabolize homocysteine properly. When MTHFR mutations are suspected, a doctor might also utilize a genetic test in addition to observing physical and mental symptoms.
Final Thoughts on Homocysteine Levels
- Homocysteine is a chemical in the blood that’s produced when an amino acid called methionine is broken down in the body.
- Causes of high homocysteine include eating a poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, smoking or drug use, nutrient deficiencies, or having a genetic defect called an MTHFR mutation.
- Elevated homocysteine levels can cause increased inflammation, irritation of the blood vessels, heart disease, neurological problems and other symptoms.
- Natural treatments for high homocysteine include improving your diet, exercising, managing stress, reducing deficiencies and taking supplements to mitigate symptoms.







