This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Gonorrhea Symptoms + 9 Natural Ways to Relieve Them
August 7, 2017

According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 820,000 new cases of gonorrhea occur each year in the United States, with 570,000 of the cases being in young people ages 15 to 24. Worldwide, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there are currently 78 million people infected. (1, 2)
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by bacteria that is spread through contact with the penis, vagina, anus or mouth of an infected partner. During childbirth, an infected mother can also transmit gonorrhea to the baby.
In a recent release from the WHO, gonorrhea is becoming more and more difficult to treat. In fact, three new superbug strains have been identified that cannot be killed by antibiotics currently on the market. These strains have been found in Japan, Spain and France. It isn’t if these strains spread across the globe, it is when. In addition, antibiotic resistant bacteria have been identified in an additional 77 countries across the world.
As of November 2017, the first case of ceftriaxone-resistant gonorrhea was documented in North America in Quebec, Canada. Ceftriaxone is an injectable antibiotic and is part of the current standard gonorrhea treatment. Experts are concerned that treatment is becoming less and less effective and that there may come a point where older antibiotics with harsh side effects may be necessary. (3)
Earlier in 2017, the WHO identified 12 bacteria that pose a risk to human health and that need further research and development of new antibiotics to cure them. The bacteria that causes gonorrhea, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, is one of them. The WHO lists it in the same priority category as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecium, Helicobacter pylori, Campylobacter, and Salmonella. The only higher priorities are Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacteriaceae. (4)
The Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership was launched by the World Health Organization to investigate and research new treatments to what they call “neglected diseases.” It is this partnership that’s leading up the fight and accelerating the development of new drugs to fight the bacteria that cause gonorrhea and other serious drug-resistant infections. (5)
Until new treatments are found for the new emerging strains, safe sex simply must be a priority for everyone. If you are diagnosed with gonorrhea, it is imperative that you retest in the months after treatment to ensure that the bacteria were sufficiently killed. There are still strains that will be cured by current antibiotic protocols, so following best practices for treatment remains a wise choice.
Gonorrhea symptoms in both men and women can mimic other conditions, and many people are asymptomatic, with no symptoms present. This presents a problem as left untreated gonorrhea can cause serious and permanent health concerns. For women, pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility, and ectopic pregnancies are possible. In men, epididymitis leading to infertility is possible, and for both sexes life-threatening cases of DGI — disseminated gonococcal infection — are possible.
The CDC recommends testing for all sexually active women under 25 years old, as well as women with multiple sex partners, regardless of age. The CDC does not make recommendations for heterosexual men. However, anyone with multiple sex partners, or who experiences any gonorrhea symptoms, should have an examination and be screened for STDs, including gonorrhea.
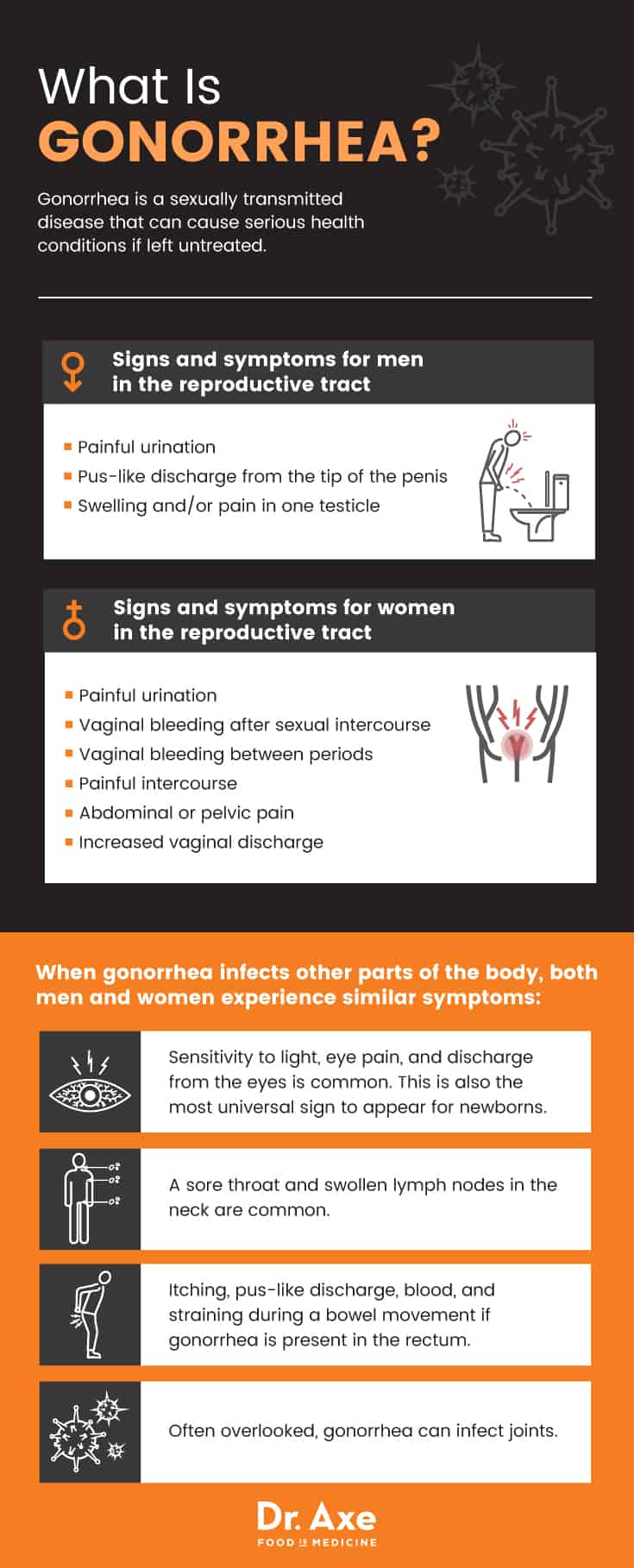
What Is Gonorrhea?
Caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium, gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that can cause serious health conditions if left untreated. The bacteria infect the urethra in both men and women and the mucous membranes of the reproductive tract in women. This includes the fallopian tubes, vagina, uterus and the cervix. Likewise, the infection may be present in the rectum, throat, eyes and mouth of both sexes. (6)
Gonorrhea can also spread through the bloodstream, leading to additional problems. Because so many people don’t experience symptoms, spreading gonorrhea to uninfected partners is quite common. Oral contact, including kissing and oral sex, vaginal intercourse and anal intercourse can all transmit the bacteria to a partner.
During childbirth, a mother can pass gonorrhea to the baby. This most commonly results in an infection in the eyes. However, other infections can develop if left untreated. Pregnant women should be tested, even if they don’t have any gonorrhea symptoms and don’t have elevated risk factors. Gonorrhea can be silent and symptom-free for years.
Gonorrhea is a curable STD, although new strains of the bacteria that cause it are emerging, showing signs they are becoming resistant to antibiotics. Researchers are concerned that with the continued evolution of the bacteria, and the global nature of gonorrhea, it is likely that gonorrhea will worsen and the potentially severe complications will become a silent epidemic.
A report published in the journal Clinical Microbiology Reviews co-authored by the World Health Organization and the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine states that genetic testing of infected individuals in specific regions and for specific strains may result in better, more targeted strain specific therapies in the future. However, the report states that crucial action and additional research is desperately needed. (7)
Gonorrhea Symptoms
In the majority of cases, gonorrhea causes no symptoms. And, unlike other sexually transmitted diseases, if symptoms do appear, they are typically more widespread, affecting multiple areas of the body. The symptoms of gonorrhea present differently in men and women because of the differences in our anatomies.
Researchers indicate that if gonorrhea symptoms are going to appear, they will develop within the first 10 to 14 days after exposure. For both men and women, the first sign may be a change in the frequency of urination, pain or burning during urination, and potentially cloudy urine.
Signs and symptoms for men in the reproductive tract include: (8)
- Painful urination
- Pus-like discharge from the tip of the penis
- Swelling and/or pain in one testicle
Signs and symptoms for women in the reproductive tract include:
- Painful urination
- Vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Painful intercourse
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Increased vaginal discharge
When gonorrhea infects other parts of the body, both men and women experience similar symptoms. (9)
- Sensitivity to light, eye pain, and discharge from the eyes is common. This is also the most universal sign to appear for newborns.
- A sore throat and swollen lymph nodes in the neck are common.
- Itching, pus-like discharge, blood, and straining during a bowel movement are common for both sexes if gonorrhea is present in the rectum.
- Often overlooked, gonorrhea can infect joints. This condition is called septic arthritis. Joints can become warm, swollen and extremely painful.
Risk Factors
Any sexual contact that involves the mouth, vagina, penis or anus can spread the gonorrhoeae bacterium that causes gonorrhea. Risk factors include: (10)
- New sexual partner
- A sex partner with multiple sex partners
- Multiple sex partners
- Failure to use condoms or improper use of condoms
- A sexual partner with a history of any sexually transmitted infection
- Alcohol use or abuse
- Illegal drug use or abuse
- If you’ve been treated for other STDs in the past
- If you are between the ages of 15 and 24
- Previous gonorrhea diagnosis
Conventional Treatment
To diagnose a gonorrhea infection, the most common procedure is a gram stain screening where a sample of tissue or discharge is examined under a microscope. While it is definitely the fastest option, it is not always accurate. In fact, while it can detect Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium, in men that are asymptomatic, it may not detect this STD.
The most accurate testing is a DNA test called the nucleic acid amplification test, or NAAT. If you are concerned about gonorrhea, ask your healthcare provider for this test as many of the symptoms of gonorrhea are similar to chlamydia symptoms, but the two require different courses of antibiotics and treatment. (11)
Once diagnosed, conventional treatments focus on killing the infection with antibiotics. There are emerging strains of drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium, and retesting after treatment has ended is absolutely necessary. The CDC recommends the antibiotic injection ceftriaxone, used in combination with oral antibiotics azithromycin or doxycycline. Babies born with gonorrhea will also be treated with antibiotics. (12)
It is important that if you test positive for gonorrhea, that you also be tested for other STDs and STIs including chlamydia and HIV.
After you and your sexual partners have completed treatment for gonorrhea, it is best to abstain from sexual contact for seven days. If you do elect to have sex during treatment or in the week following treatment, properly use a condom during all sexual contact. Remember, gonorrhea can spread through oral sex, vaginal sex and anal sex. (13)

9 Natural Treatments for Gonorrhea Symptoms
As bacteria continue to morph and become more and more resistant to conventional antibiotics, emerging research is underway to look into new antimicrobial agents. Researchers from the University of Ottawa are examining the use of certain Canadian botanicals commonly used by First Nations as medicinal plants in the treatment of gonorrhea. Kinnikinnick, goldenseal, black cherry, roseroot, and others are being studied, lending hope that effective treatments for drug-resistant bacteria may be on the horizon. Until then, following a doctor’s prescription and supplementing it with natural treatments and remedies for the symptoms of gonorrhea is the best course of action.
1. Berberine. Of particular interest in the Canadian study referenced above, researchers indicated Berberine — specifically from H. Canadensis, or goldenseal — inhibited the growth of all Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in the study. Researchers note that further exploration is necessary but that botanicals do represent a potential source of compounds to inhibit the bacteria responsible for gonorrhea, even those resistant to antibiotics. (14)
When undergoing treatment for gonorrhea, adding a high-quality berberine supplement may be helpful to combat gonorrhea symptoms. Take 500 milligrams three times each day. It is considered safe. However, if you take medications to lower blood glucose levels, it is not recommended. Side effects are typically minor for most people and include gastrointestinal issues like flatulence, pain, constipation, cramping or diarrhea.
2. Goldenseal. Another powerful native herb, research shows that goldenseal demonstrates antibiotic properties and even fights cancer. Adding it to your gonorrhea treatment is a safe and effective way to boost your immune system’s response to the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. If you have high blood pressure, heart disease, liver disease, or you are pregnant or breastfeeding, goldenseal should be avoided. If you elect to take a high-quality berberine supplement as mentioned above, adding additional goldenseal is not necessary. However, if you can’t locate a reputable source for berberine extracted from goldenseal, a goldenseal supplement is the next best thing.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar. ACV is known to fight infections, certain types of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and it can be helpful for overcoming gonorrhea symptoms. Topically, apple cider vinegar can be applied to affected areas with a cotton ball, or you can add a couple of cups to a bath and soak for 20 minutes. For women who have vaginal gonorrhea, soaking an organic tampon in apple cider vinegar may help to kill the infection.
From the inside, drinking an ACV elixir will add good bacteria to your system to help fight any bad bacteria. Try my favorite secret detox drink recipe, which contains apple cider vinegar, lemon juice, cinnamon and cayenne pepper. These ingredients can strengthen your immune system’s response and balance your body’s pH.
4. Echinacea. Steeped in native healing practices worldwide, echinacea is the perfect accompaniment to gonorrhea treatment protocols and to lessen common gonorrhea symptoms. From colds and flu to pain and even snake bites, the Echinacea helps our immune system function optimally. In fact, the USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service recommends a dosage of 10 milligrams per kilogram of body weight for 10 days to stimulate the immune system. (15)
5. Epsom Salt. A powerful detoxifier — and used for generations as an anti-inflammatory and pain reliever — Epsom salt baths may help alleviate some of the symptoms of gonorrhea. While viral infections, including herpes, are more commonly treated with Epsom salts, adding a couple of cups to bathwater and relaxing for 20 minutes or longer, can help cleanse the mucous membranes affected by gonorrhea or other STDs.
6. L-Arginine. With impressive inflammation fighting and detoxification properties, the amino acid L-arginine also demonstrates antibacterial properties. Studies show that it can inhibit the growth of certain bacterial infections. In addition, it can help to lower inflammation which can be especially useful for those with gonorrhea experiencing joint pain and septic arthritis.
Taking 1,000 milligrams each day during gonorrhea treatment, and supplementing with foods rich in this amino acid can help ease symptoms. Add sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, cage-free eggs, kefir, organic organ meats, and wild-caught fish to your diet an added boost L-arginine.
7. Probiotics. Whenever you are fighting a bacterial infection or virus, upping your intake of probiotic foods is wise. Kefir, sauerkraut and kimchi, kombucha, yogurt and apple cider vinegar are just a few great sources to introduce healthy bacteria into your system to join the fight against the unhealthy bacteria causing the infection.
In addition, taking a high-quality probiotic supplement formulated from soil-based organisms offering at least 50 billion CFUs per serving can help your body more effectively fight unhealthy bacteria, wherever they are in your system.
8. Raw Honey. If gonorrhea has infected the throat, adding a tablespoon of raw honey to warm — not hot — water or tea, can relieve sore throat pain. In addition, it is known to fight dozens and dozens of types of bacteria; however, no detail is available on its effect on Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. For 1,000s of years, raw honey has been an effective treatment for wound healing, for gastrointestinal upset, fungal and viral infections, and as an anti-inflammatory. (16)
9. Black Tea. Globally, one of the most popular drinks, black tea shows impressive antibacterial activity. Using it as the basis of raw honey drinks is a great way to absorb the health benefits of the world’s most popular drink. (17)
If gonorrhea has infected the eyes and there is oozing of pus, a black tea compress may help to fight the infection and relieve the discomfort. Soak a high-quality black tea bag in very warm water to activate the oils in the tea leaves for one minute. Gently squeeze out the excess water, leaving it just barely moist. Place it on your eye, and relax for 20 or 30 minutes, allowing the tea to soak in. Some people may find a touch of stinging or burning at the beginning, but this just shows that it is working.
Precautions
Complications can occur if gonorrhea is not treated, some which are dangerous and even life-threatening.
Infertility in both men and women, pelvic inflammatory disease, and epididymitis are possible complications if left untreated.
If Neisseria gonorrhoeae spreads through the bloodstream, which it can, gonorrhea can infect other parts of the body including your joints, leading to septic arthritis. Watch for severe joint pain, stiffness, swelling, as well as a fever and mention any of these symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Men who have had gonorrhea are associated with an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. Researchers note this applies in particular to African Americans. (18)
When an infant is born with gonorrhea, possible complications include blindness, infections, and sores on the scalp. If you are pregnant and have had gonorrhea in the past, be sure to mention it to your OB-GYN team.
A Note About Condom Usage and Communication:
The American Sexual Health Association recommends that latex condoms be used from the very beginning of sexual contact until there is no longer skin to skin contact to reduce the risk of transmission of gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted diseases. (19) STDs can be transmitted during oral sex too. Condoms or dental dams should be used during all oral sexual activity. The CDC’s The Right Way to Use A Male Condom and The Right Way to Use A Female Condom cover best practices from basic “how to’s” to checking for expiration dates, and proper disposal.
If you are diagnosed with an STD, it is essential that you inform all your sexual partners and that they inform all their sexual partners. There is a reason that these diseases spread so rapidly through schools and colleges, and even nursing homes — often people are shy and embarrassed to discuss sexual health, even when they are sexually active.
Remember, it is much easier to talk about safe sex with a partner than it is to talk about a positive STD result. Open and honest communication from the start can save you and your partner from awkward conversations in the future and hopefully hinder the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases and infections.
For teens and young adults, open lines of communication between a trusted adult (hopefully a parent) and the teen is vital for their sexual health. Teens are engaging in sexual activities earlier than ever before. In fact, a CDC survey of U.S. high school students in 2015 found that 41 percent of those surveyed had had sexual intercourse. And, nearly half, 43 percent, did not use a condom the last time they had sex. (20)
There are many resources available to help you talk to your children about sex and practicing safe sex. The Mayo Clinic offers hints to break the ice with your teens. Invite a discussion, and encourage your teens to ask questions now or at any point in the future. (21)
Final Thoughts
- 78 million people worldwide are believed to currently have gonorrhea.
- New, emerging strains are drug-resistant, making it difficult to cure.
- If you have any gonorrhea symptoms, ask your doctor for the NAAT test, the most reliable test available.
- Gonorrhea and chlamydia share similar symptoms. However, they each require different types of antibiotic treatments.
- Many people do not experience gonorrhea symptoms; if symptoms are going to appear, they typically develop within the first seven to fourteen days after exposure to the bacteria.
- Left untreated, gonorrhea can cause potentially serious, and even life-threatening conditions.
- Routine screenings are a must for anyone who has multiple sexual partners, or if your partner has multiple sex partners.
- Re-screening after completing antibiotic treatment is essential to ensure that the bacteria has been killed.
- Communicating with current and past sexual partners after a diagnosis of an STD, including gonorrhea, is vital.
- The only way to prevent STDs is abstinence; however, proper and routine use of condoms during oral, vaginal, and anal sex can help thwart stubborn and potentially dangerous infections.





