This Dr. Axe content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure factually accurate information.
With strict editorial sourcing guidelines, we only link to academic research institutions, reputable media sites and, when research is available, medically peer-reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
This article is based on scientific evidence, written by experts and fact checked by our trained editorial staff. Note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, etc.) are clickable links to medically peer-reviewed studies.
Our team includes licensed nutritionists and dietitians, certified health education specialists, as well as certified strength and conditioning specialists, personal trainers and corrective exercise specialists. Our team aims to be not only thorough with its research, but also objective and unbiased.
The information in our articles is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.
Cassia Oil Benefits for Circulation, Arthritis, Depression & More
April 21, 2025

Cassia oil, a warm and spicy essential oil derived from the bark of the Cinnamomum cassia tree, has been treasured for centuries for its powerful therapeutic properties. Often overshadowed by its close relative, cinnamon, cassia oil holds its own with a rich profile of health benefits that range from supporting immune function to easing digestive discomfort.
With its bold aroma and potent natural compounds, cassia oil is more than just a fragrant addition to aromatherapy; it’s a time-tested remedy that continues to find its place in modern wellness routines.
So read on to explore the many benefits of cassia oil and how it can enhance your health and well-being, naturally.
What is cassia oil?
Cassia is considered one of the 50 fundamental herbs in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). It’s an evergreen tree native to China and Burma.
Cassia is commonly known as Chinese cinnamon, and its scientific name is Cinnamomum cassia. Cassia essential oil, or cassia bark oil, is derived by steam distillation of the cassia bark, leaves and twigs.
Cassia is similar to true cinnamon (sometimes called Ceylon cinnamon) and mimics some cinnamon benefits and uses. They’re from the same botanical family, and they both have a spicy, warm aroma. However, cassia bark oil is sweeter than cinnamon.
Cassia has been used extensively in indigenous and folklore medicine systems. In the Indian system of medicine, known as Ayurveda, the plant has been documented as thermogenic, purgative, expectorant and diuretic, and it’s been used in the treatment of leprosy, erysipelas, ulcer symptoms, cough, flatulence, dyspepsia, menstrual problems and tuberculosis.
It’s also been used as a bronchitis natural remedy, anemia natural treatment and for natural constipation relief.
Cassia oil, like frankincense oil, myrrh and several other oils, is also included in the Bible as an important essential oil.
Cassia oil can be used for cleaning and cooking, but the health benefits of using this powerful oil are really surprising. Cassia oil is known to boost the immune system, helping the entire body run properly.
It helps maintain a healthy and functioning digestive system and improve blood circulation, as well. Cassia oil is also an antidepressant, and it has been used for years to build courage and a sense of self-worth.
It has a warming effect on the body and keeps your mind at peace.
Cassia is cultivated in southern and eastern Asia, including India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam. In the United States, the United Kingdom and India, cassia is the most common type of cinnamon used.
Cassia is an evergreen tree from the Cinnamomum family that grows to be around 32 feet tall. The bark is a gray color and the leaves are hard and elongated, growing to be about four inches long.
Cassia bark, both powdered and in “stick” form, is used as a flavoring agent for confectionery, desserts, pastries and meat. It’s also specified in many curry recipes.
Typically, cassia is sold as pieces of bark or sticks, but it’s easy to find cassia bark oil in your local health food store. The chief constituents of cassia oil are benzaldehyde, chavicol, cinnamic aldehyde, cinnamyl acetate and linalool.
The flavonoids and antioxidant polyphenolic compounds in particular are known to scavenge the formation of free radicals and have great potential in ameliorating disease processes like cancer and diabetes.
Benefits
1. Helps treat diarrhea
Diarrhea is a natural reaction to toxins that need to be expelled from the digestive system. Luckily, cassia oil is an anti-diarrhea agent that’s able to bind bowels and stop diarrhea episodes.
More specifically, cassia oil kills microorganisms that sometimes lead to diarrhea, and it helps stiffen stool with its fiber content. It serves as a natural way to alleviate diarrhea because of its warming, bacteria- and fungi-killing, body-soothing, and anti-inflammatory properties.
A randomized, controlled trial published in 2023 investigated the effects of cinnamon water extract (CWE) from Cinnamomum cassia on individuals experiencing diarrhea symptoms. Conducted over eight weeks, the trial involved 70 participants who received either CWE or a placebo.
Here were some key findings:
- Improved gastrointestinal function: Participants consuming CWE exhibited a significant increase in colonic transit time, indicating a normalization of bowel movements.
- Altered fecal metabolites: CWE intake led to higher levels of fecal isobutyric acid and spermidine, while reducing indole and agmatine levels.
- Enhanced gut microbiota diversity: There was an increase in the diversity of gut microbiota, notably a rise in Bifidobacterium longum ATCC 55813, which correlated positively with improved colon transit time and beneficial stool metabolites.
These results suggest that cassia oil may alleviate diarrhea symptoms by modulating the gut environment, including microbial composition and metabolic activity.
2. Improves circulation
By improving the circulation of blood throughout the body, cassia oil ensures that you get the proper amounts of nutrients and oxygen in order to thrive. Cassia oil enhances blood circulation, creates a feeling of warmth in the body, alleviates pain, reduces disease-causing inflammation and promotes urination, enabling the body to shed toxins.
Muscle aches, for example, are caused by weak circulation, increased physical activity, stress, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal changes and dehydration. Some of the most common areas for muscle aches include the lower back, neck, trapezius and legs.
Because cassia oil stimulates circulation and works as an anti-inflammatory agent, it serves as a natural muscle ache treatment. By improving circulation, cassia oil also helps lower the risk of stroke and heart attack, two life-threatening occurrences that can be avoided with this powerful oil.
3. May relieve menstrual symptoms
Cassia oil helps open obstructed menstrual paths so it can relieve the cramps that are common when menstruating and potentially keep your cycle regular. It also helps naturally remedy PMS cramps and menstrual symptoms, such as headaches, fatigue, muscle aches, moodiness and bloating.
The emmenagogue, analgesic and pain-relieving properties of cassia oil allow it to combat irregular periods and painful symptoms.
Cassia oil is also an antiemetic oil known as a natural remedy for nausea and helps reduce the occurrence of vomit. This can be helpful during PMS and menstruation or at any time you feel nauseous.
By reducing inflammation and bloating, and relaxing the body and mind with its warming effects, cassia oil is the perfect treatment for those unwelcome menstrual symptoms.
4. Can help manage arthritis symptoms
Because arthritis causes swelling and pain in the joints, cassia oil’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce arthritis symptoms naturally.
A study published in the Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research tested the active components of cassia oil and found that a compound called cinnamaldehyde not only inhibited inflammatory mediators, but also activated anti-inflammatory mediators in a lab setting.
Inflammation has been found to be associated with just about every health condition, so not only does cassia oil help relieve symptoms of arthritis, but it impacts all bodily functions and systems.
5. Combats stress
Cassia oil is an effective antidepressant that has the power to bust stress, leaving the body feeling warm and tranquil. It contains cinnamic aldehyde, a component that has been studied in both humans and animals and is known to alleviate stress-induced behaviors and conditions.
Stress and anxiety have a much bigger impact than most people think. They can influence every system of the body and wreak havoc on its daily functions, while chronic stress can kill your quality of life.
By inhaling or diffusing two to three drops of cassia oil, you can ease your nerves and allow your body to work properly. So make cassia oil part of your depression diet if you suffer from this condition.

6. Boosts immune system
Cassia oil is an antimicrobial and antiviral agent. It also works as a febrifuge, fighting infections that cause fever.
This powerful oil helps protect the urethra, colon, kidneys and urinary tract from microbial growth and infections. It also protects the body from viral diseases and conditions such as influenza, cough and the common cold.
In addition, cassia oil has a warming effect on the body, so it relieves the body of tension and is able to lower body temperature by killing infections that cause inflammation and fever. At the same time, it works as a stimulant, keeping your brain alert and activating bodily functions.
7. Fights bacteria
A study published in the American Journal of Chinese Medicine found that both oil and pure cinnamaldehyde (the organic compound that gives cassia its flavor and odor) were equally effective in inhibiting the growth of various isolates of bacteria. The study tested cassia’s efficacy against bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella typhimurium, plus fungi-including yeasts (four species of candida), molds and dermatophytes.
These findings prove that cassia oil serves as an antimicrobial and antibacterial agent that protects the body from dangerous infections.
8. Works as an astringent
Due to its astringent properties, cassia oil potentially can help treat sore throat, external and uterine hemorrhaging, peptic ulcers, and diarrhea. It causes the shrinkage of mucous membranes or exposed tissues. Internally, it can stabilize the discharge of blood serum or mucous secretions.
Cassia oil’s astringent properties also make it a useful oil for skin and hair health. It protects the skin and can be used to naturally treat acne, heal wounds and sores, naturally remedy rashes, and treat skin irritations. It also strengthens hair roots, gums and helps tighten muscles.
9. Natural bug repellant
A study published in Pest Management Science tested the efficacy of cassia oil in repelling yellow fever mosquitoes. Four human volunteers were exposed to the mosquitoes in an indoor test that lasted 30 minutes.
Cassia oil use led to a 94 percent protection. More specifically, at 50 minutes cassia oil provided 83 percent protection, and at 70 minutes it provided 61 percent protection.
The results indicate that cassia oil is effective as a mosquito repellant and works as an all-natural and chemical-free remedy.
10. Might aid blood sugar levels
Cassia oil has been getting a lot of attention for its ability to potentially help naturally treat diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels. Some studies have suggested that this is true, but the research is mixed.
A notable human clinical trial examining the effects of Cinnamomum cassia, for instance, found this oil shows promise for diabetics in some aspects but is not a cure-all.
In this study, 18 adults aged 40-65 with type 2 diabetes (diagnosed within the past year and treated with metformin) were randomly assigned to receive either 1,000 milligrams of cassia cinnamon or a placebo three times daily before meals for 12 weeks. The results demonstrated that participants taking cassia cinnamon experienced statistically significant reductions in body weight, body mass index and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels.
However, no significant changes were observed in fasting glucose, blood pressure, lipid profiles, arterial stiffness or endothelial function.
More research is needed to determine the potential of cassia oil as an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, but the increased interest in this oil’s ability to naturally treat such problematic conditions is very promising.
How to use
Cassia oil can be used just like common cinnamon oil. It can be ingested or used topically, or you can diffuse it.
When consuming cassia oil, start with small doses (a drop or two), and work your way up from there. It provides a spicy and warm flavor that goes perfectly with teas, coffee and spicy dishes.
Here are some cassia oil uses that you can try at home:
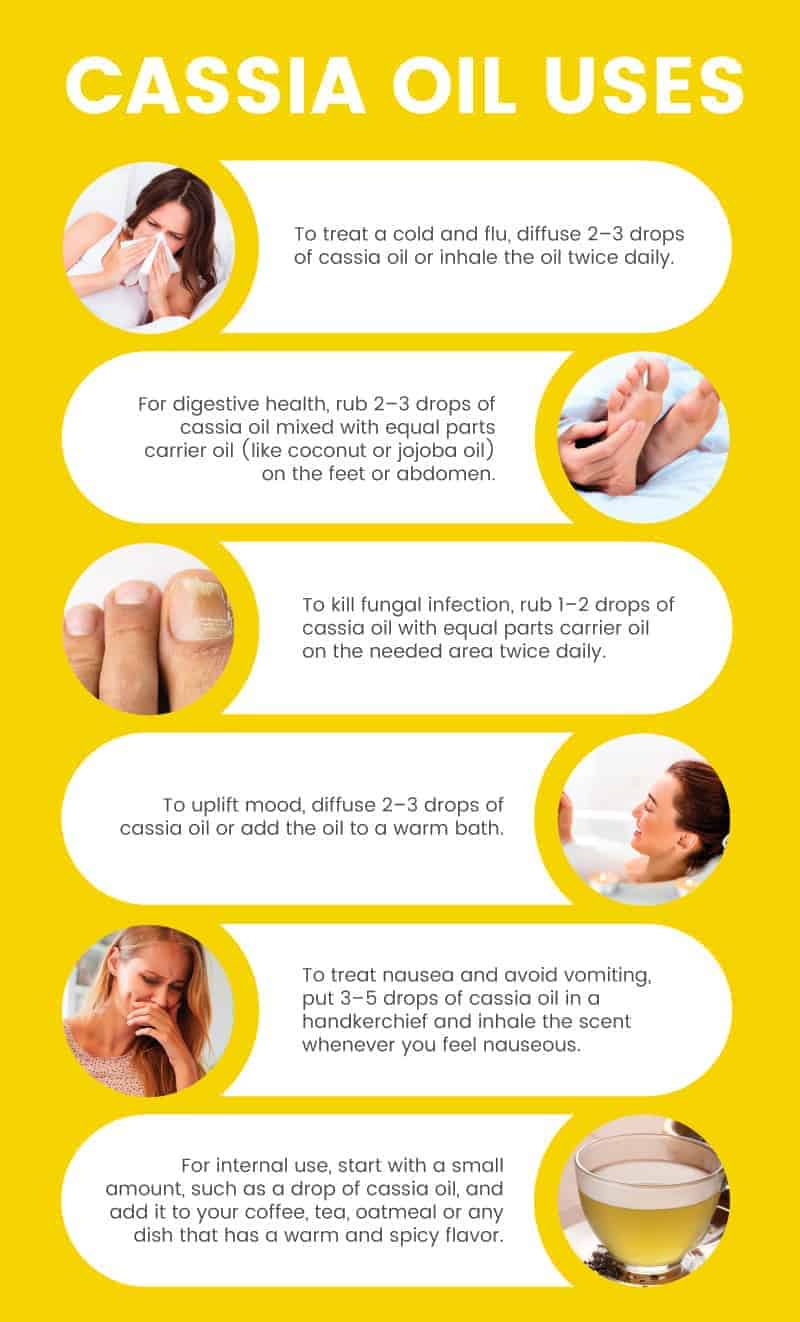
- To treat a cold and flu, diffuse two to three drops of cassia oil, or inhale the oil from the bottle twice daily.
- For digestive health, rub an oil blend of two to three drops of cassia oil mixed with equal parts carrier oil (like coconut or jojoba oil) on the feet or abdomen.
- To kill fungal infection, rub a dilution of one to two drops of cassia oil with equal parts carrier oil on the desired area twice daily.
- To uplift mood, diffuse two to three drops of cassia oil, or add the oil to a warm bath.
- To treat nausea and avoid vomiting, put three to five drops of cassia oil in a handkerchief, and inhale the scent whenever you feel nauseous.
- For internal use, start with a small amount, such as a drop of cassia oil, and add it to your coffee, tea, oatmeal or any dish that has a warm and spicy flavor.
There are a ton of ways to incorporate cassia oil into your daily routine, whether it’s in the kitchen or part of your beauty and bathing regimen. Here are a few more ideas to get you started:
Add one to two drops of cassia oil to this Baked Apple Cinnamon Oatmeal recipe. This is a great idea for breakfast. It keeps you full because it’s packed with fiber, and with the addition of cassia oil, it has an extra anti-inflammatory punch.
If you want to cleanse, lose body fat, boost energy and help manage disease, then adding natural detox drinks to your diet can help you improve your quality of life. Add one to two drops of cassia oil to this Secret Detox Drink, and watch (and feel) the magic happen.
Take advantage of the calming and warming qualities of cassia oil. This Homemade Healing Bath Salts recipe will help increase relaxation, relieve muscle pain, decrease stress and support body detoxification.
Rather than spend hundreds of dollars at the spa, try this amazing spa-like recipe in the comfort of your own home. Try adding five to 10 drops of cassia oil to the recipe for optimal results.
Risks, side effects and interactions
Cassia oil is safe for topical and internal use.
It should be avoided during pregnancy because it may produce irritation and sensitization on the skin and in the mucous membrane. It may also reduce the secretion of milk, so it’s not recommended for mothers who are lactating.
Taking large amounts of cassia cinnamon might cause side effects in some people. The oil contains large amounts of a chemical called coumarin, and some people are sensitive to coumarin.
When applied to the skin, cassia oil can sometimes cause skin irritation and allergic skin reactions, so try testing the oil on a small patch of skin first.
Cassia oil might decrease blood sugar, so taking cassia oil along with diabetes medications might cause your blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely if you are using both.
Some medications used for diabetes include glimepiride (Amaryl), glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase PresTab, Micronase), insulin, pioglitazone (Actos), rosiglitazone (Avandia), chlorpropamide (Diabinese), glipizide (Glucotrol), tolbutamide (Orinase) and others.
Taking very large doses of cassia cinnamon might harm the liver, especially in people with existing liver disease. Do not take large amounts of cassia cinnamon if you are taking a medication that can harm the liver.
Some medications that can harm the liver include acetaminophen (Tylenol and others), amiodarone (Cordarone), carbamazepine (Tegretol), isoniazid (INH), methotrexate (Rheumatrex), methyldopa (Aldomet), fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Sporanox), erythromycin (Erythrocin, Ilosone, others), phenytoin (Dilantin), lovastatin (Mevacor), pravastatin (Pravachol), simvastatin (Zocor) and many others.
Frequently asked questions
What is cassia oil used for?
Cassia oil is commonly used for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and warming properties. It’s often used in aromatherapy, massage oils and topical blends for muscle pain relief.
It can also support immune health, improve circulation and help with digestive issues.
What does cassia do to the body?
Cassia can stimulate the body in several ways, including:
- Promotes blood circulation
- May support digestive health
- Can create a warming sensation when applied to the skin
- Acts as a natural antimicrobial
However, it is very potent and can cause skin irritation or sensitivity if not properly diluted.
What is cassia oil in the Bible?
Cassia is mentioned in the Bible as one of the ingredients in sacred anointing oil (Exodus 30:24). It symbolized purification, sanctification, and was associated with worship and holiness. It was considered precious and used in spiritual rituals.
Is cassia oil the same as cinnamon?
Not exactly. Cassia oil comes from Cinnamomum cassia, while true cinnamon oil is from Cinnamomum verum (or zeylanicum).
They are closely related, and both have warm, spicy aromas. However, cassia is generally stronger, more pungent, and more intense in both scent and effect.
What are the risks of using cassia essential oil?
- Skin irritation or burns if not diluted
- Sensitization or allergic reaction in some people
- Should be avoided by pregnant women, young children and people with liver conditions
- Can be toxic in large doses
Always dilute with a carrier oil, and do a patch test before use.
What does cassia oil smell like?
Cassia oil has a warm, spicy, sweet and slightly woody aroma, very similar to cinnamon but more intense and sharper. It’s often described as hotter or more fiery than cinnamon oil.
What is cassia oil good for?
- Boosting the immune system
- Easing joint and muscle pain
- Stimulating digestion
- Reducing stress and fatigue
- Supporting circulatory health
- Adding a warming scent to perfumes and diffusers
Conclusion
- Cassia essential oil stands out as a multifaceted natural remedy with a rich history in traditional medicine.
- Its diverse therapeutic properties, ranging from improving circulation and alleviating arthritis symptoms to enhancing mood and supporting digestive health, make it a valuable addition to holistic wellness practices.
- Whether used aromatically, topically or internally (with appropriate caution), cassia oil offers a warm, spicy aroma and a host of health benefits.
- As with all essential oils, it’s important to use cassia oil responsibly, considering potential side effects and interactions.
- Incorporating cassia oil into your daily routine can be a natural way to support overall well-being.









